One of the first things a user notices about your website is how long it takes to load. The faster it is, the happier they are.
More than 73% of mobile internet users claim they encountered websites that take too long to load. This is why page speed is one of the most important ranking factors determining your web page’s position in Google search results. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights have been beneficial in quantifying this aspect of user experience.
Your web page should load in less than three seconds to encourage users to spend as much time on your website as possible. PageSpeed optimization improves your rankings and provides a better web experience for users.
Today, we’ll review how you can use Google PageSpeed Insights to your advantage and leave a lasting impression on your audience. You’ll learn how to improve your Google PageSpeed scores and use it to improve your website.
Your Run-Through of Google PageSpeed Insights
Google PageSpeed Insights provides you with both lab data and field data. Lab data is collected in a controlled environment and is beneficial in identifying your website’s performance issues. On the other hand, field data is collected from the actual and real-time performance analytics when users load the web page.
The Google PageSpeed Insights tool gives you performance, accessibility, best practices, and SEO scores out of 100. It also provides you with a Core Web Vitals assessment, which is determined by your website’s performance and speed.
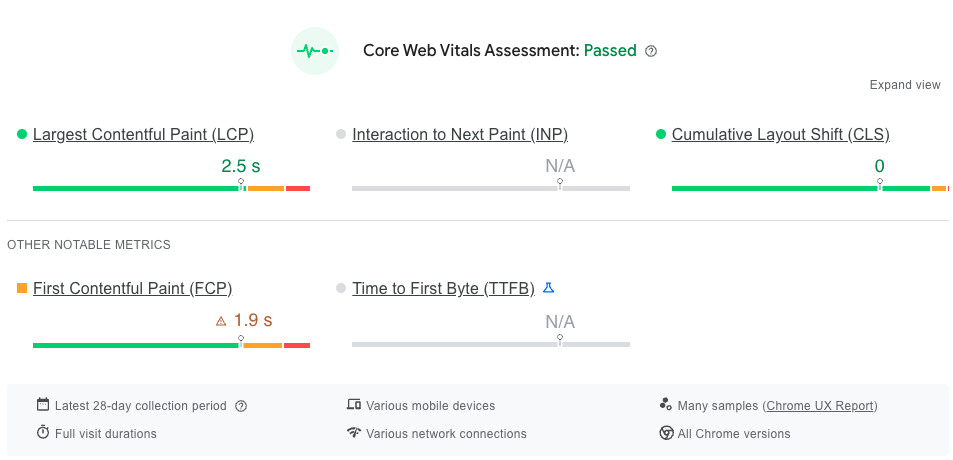
Let’s review the performance score out of 100. The PageSpeed Insights performance score is calculated using the following metrics:
- First contentful paint
- Largest contentful paint
- Total blocking time
- Speed index
- Cumulative layout shift
The accessibility, best practice, and SEO scores all have specific metrics that can be uncovered when running your website’s URL through this test: simply paste the URL you want to test and click analyze. Once the test is complete, Google PageSpeed Insights displays a performance report. This report is classified into three groups and indicates your website’s overall performance.

Why Does Page Speed Matter?
Today’s internet users are looking for quick answers and solutions. This is why websites are expected to be as fast as possible.
Apart from enhancing page experience, page speed has become one of the top 200 most important ranking factors to reflect how important it is for a website’s UX.
Speed is not just a ranking factor—there is a direct correlation between having a faster website and more conversions. A 2019 study by Portent found a connection between speed and higher conversion rates. The study showed that with each additional second of load time (between seconds 0 and 5), conversion rates dropped by an average of 4.42%. The study also found that the first 5 seconds of page speed affect conversion rates the most.
All these studies demonstrate the importance of speed – even a minor improvement to your website’s Google PageSpeed can positively impact your business.
Resource: PageSpeed Tips and Statistics You Need to Know
Is Google’s PageSpeed Insights Accurate?
Google’s PageSpeed Insights includes different metrics to offer an accurate overview of your website’s performance. Recent changes over the last several years have improved its reliability and accuracy even more.
An earlier iteration of Google’s PageSpeed Insights, Google PageSpeed 5.0, was released in November 2018 and began using the Chrome User Experience Report database and Lighthouse audits.
Two years later, in May 2020, Lighthouse 6.0 was introduced with new metrics. These metrics improved the tool’s overall performance and captured the user experience better. By 2023, Google had rolled out Lighthouse 11, which featured new audits, bug fixes and changes to scoring.
They will continue to upgrade and enhance this tool to make it more reliable. This is why you can confidently rely on your Google PageSpeed score to assess how well your website performs and interacts with users. Additionally, this tool provides recommendations for improving the weaker areas of your website. You can use these insights to enhance the user experience and boost your Google PageSpeed score.
Google PageSpeed Vs. WebPageTest Vs. GTMetrix
Although Google PageSpeed Insights is a reliable tool for assessing your website’s performance, it isn’t the only option available. Other alternatives, such as GTMetrix, WebPageTest, and Pingdom, can also be used to test page speed. Let’s explore these tools to better understand the key differences between them.
Google PageSpeed Insights
This tool shows two main tabs—one for desktop and one for mobile. Page speed also does a great job of offering specific actions that improve your score and user experience.
The PageSpeed tool is self-contained, meaning you cannot create an account and track your results over time. The only option users have to measure their performance over time is to continually run manual tests at intervals.
PageSpeed can identify problems bringing down your search rankings, like:
- a lack of caching policy,
- a high number of third-party requests,
- excessive DOM structures, etc.
Although the tool offers actionable ways to improve your website’s speed, it leaves a small window for customization. You will not be able to specify more specific parameters like server location or connection throttling, and these parameters are not reported.
WebPageTest
This page speed optimization tool conducts three tests and presents the results in median statistics.
The advanced settings are applied with their default values during a standard routine test. Once the test is completed, you will receive a screenshot of the loaded website, along with an option to view the filmstrip of the test. A detailed tab provides a waterfall report that includes additional metrics and information for each test run.
WebPageTest also allows you to create custom metrics to evaluate your website based on your specific requirements. To perform a custom test, you can either specify a custom metric during the test or include a JavaScript file. This tool offers the highest level of customization compared to the other testing tools. Even in the basic testing tab, you can enter the URLs of the websites you wish to assess using the EST configuration. Additionally, the tool offers an option to conduct a Lighthouse audit.
The performance review presents a comprehensive optimization checklist for the website. It lists all the resources and compares them against the established parameters that impact the website’s performance. The site is organized into several tabs, each displaying the speed of the website. The domain, processing, and content breakdown tab shows a distribution of requests and content on the webpage, while the Image Analysis and Request Maps tabs redirect you to other services.
GTMetrix
GTMetrix has several features that allow you to test the performance of your website.
The final result of the test is distributed into three metrics: the total size of the page, page load time, and the total number of HTTP requests. A comparison is also shown between your own metrics and the average scores from all the websites tested using GTMetrix. With an ad-hoc test, you cannot specify the browser, connection setting, or test location.
Image optimization plays a significant role in ranking, and this is why videos and images must be optimized to rank your website higher. The number of HTTP requests affects your score on GTMetrix as well. The Waterfall tab, which uses the “Inspect” tool, can be used to analyze how much time was spent on each request when the page was loaded.
After creating an account on GTMetrix, you will have access to videos and graphs, and you can also perform multiple tests on your website.
How The Three Tests Compare
These three tests are the most commonly used page speed tools by developers and SEO teams to test a website’s performance, but how do these tools compare with each other?
1. Device and Browser Selection
The tests should be conducted from different devices and browsers to emulate your website’s performance on different networks, and a good testing tool should allow you to choose your browsers and devices.
- Google Pagespeed Insights: results are shown on two tabs, one for mobile and desktop — however, you don’t get many customization options to select which mobile device you want to run your test on.
- WebPageTest: you can specify a browser and a device combination. They have a variety of devices available to choose from.
- GTMetrix: GTMetrix lets you test your website from your chosen browser and device combination. However, the user will be required to create an account to customize these options.
2. Test Location
The load time varies on the location of the test and the location of the server. This is why to reach your customers in their own region, your server should be as close to their geographic location as possible. When you specify the test location, you will get the most accurate results about your website.
- Google PageSpeed Insights: you can’t specify the location of the test, as it is mostly calculated internally based on the location of your website’s own server.
- GTMetrix: allows you to specify the location of the test. They have a variety of location options that you can choose from, but you will need to register first to use this feature.
- WebPageTest: also lets you select locations when conducting a test. Almost all significant locations can be found with this tool.
3. Waterfall Analysis
A website speed testing tool should offer this important feature to help analyze the bottlenecks in the website’s design and structure. A waterfall chart usually displays the time each resource takes to load and how it affects the overall load speed of the web page.
- Both the WebPageTest and GTMetrix tools show you a waterfall chart to carefully analyze your website and how long each resource takes to load.
- The Google Pagespeed test does not include a waterfall analysis
9 Steps for Google PageSpeed Optimization

A higher score on this tool means a fast and optimized website. Achieving a perfect 100 score on PageSpeed is difficult but not impossible. With the right methods and processes, you can optimize your website’s speed and performance to achieve a perfect 100 score. Some tips that can be used to score perfectly on this test include:
1. Eliminate Render-Blocking Resources
This is one of the most common recommendations featured in the PageSpeed Insights tool. It refers to JavaScript and CSS scripts that prevent your page from loading quickly.
These files need to be processed and downloaded by the visitor’s browser before the rest of the page can be displayed. Thus, having a lot of scripts above the fold can affect the speed of your website negatively. According to Google, two solutions can be used to fix this issue.
- If you have a limited number of JavaScript or CSS files, you can inline them. This process means incorporating your CSS and JavaScript into your HTML file, which can be done through plugins. However, this method is only feasible for small websites.
- The other method is to defer your JavaScript. With this option, the JavaScript file is downloaded during HTML parsing, but it only works when the parsing is complete.
2. Minify JavaScript
Where possible, you should minify your JavaScript files the same way you would reduce the number of your CSS files. When you minify your JavaScript files, you can reduce the script parse time and payload size. These files can be minified via WordPress plugins. You can also build a process to do this minification upfront.
3. Remove Unused CSS
The code in your stylesheets is considered content and must be loaded first to make your page visible to the users. Any CSS that is not being used on your website puts an unnecessary drain on its performance. This is why it’s recommended that any unused CSS be removed.
The process is similar to eliminating render-blocking CSS. The styles can be inline or deferred in a way that suits your web pages. Tools like Chrome DevTools can also be used to find and optimize unused CSS.
4. Image Optimization
Media files like videos, audio, and images can have a serious impact on your site’s performance if they are not accurately sized or optimized.
Optimizing your file to an acceptable size is the simplest way to reduce your page load time. If you are using large images on your page, you can use CSS to resize them and reduce their impact. However, this method can take longer than loading them at the right size from the beginning.
Upload accurately sized images or use responsive images, and create images of different sizes for specific devices. This can be done by using the srcset attribute, which is added to the image tags to specify the image files at different sizes. This list is read by the browser, and it determines the best version of your image for the screen and displays the selected version to the user.
Some other methods of optimizing include:
Compress Images
Images can significantly impact the performance of a website, which is why it’s important to optimize them. The most simple way to optimize your images is to compress them. This method reduces the size of the file and makes it load faster. This is one of the most commonly advised methods by technical SEO experts and Google itself. The goal here is to reach the smallest file size possible without compromising the quality of the image. Several plugins like Smush and Imagift can be used to achieve the desired results. Some other methods of image optimization include:
- Implementing lazy loading (deferring offscreen images until above-the-fold content is loaded)
- Using animated video formats like GIFsServing images at an accurate size
Convert To Nextgen Formats Optimized For Browsers (WebP)
Some image formats load faster than others, but they are not common formats like PNG or JPEG. WebP is a new format that is becoming the standard format for better speed and performance, and Google expects you to use it in your web pages. Google PageSpeed Insights will inform your website doesn’t adhere to this new standard.
This recommendation is challenging to meet, but several plugins can help you change the format of your images to comply with the set standards. Smush and Imagify both offer a feature that lets you convert your images to WebP format. You can use them to make the switch and make your website faster.
Defer Or Lazy Load Offscreen Images
Deferring or lazy loading images refers to the same process: loading the images that are immediately visible on page load first. The browser loads visible photos first instead of loading every single image file at once, which automatically improves the performance of the page. This is why lazy loading is recommended by Google.
5. Reduce JavaScript Execution Time
JavaScript execution can be the most prominent factor and contributor to main-thread work, and it can affect the speed and performance of your website. Google PageSpeed Insights recommends reducing the execution time separately to alert if this execution is impacting your site’s performance significantly.
6. Reduce TTFB Latency
Time to First Byte (TTFB) is a measure that determines how long it takes for the browser to receive its first byte of data back from your site’s server after it has made a request. Having a low TTFB can affect the speed of your website. This is why Google recommends reducing the server time. Some ways to reduce your TTFB include:
- Using lightweight plugins and themes
- Using a CDN (Content Delivery Network)
- Choosing a good DNS (Domain Name System) provider
- Selecting a high-quality web hosting provider that can offer improved Google PageSpeed
- Using fewer plugins on your site
- Implementing browser caching
7. Enable Text Compression
This recommendation refers to using GZIP compression. On some servers, the feature of text compression is enabled automatically. However, if it is not automatically enabled on your website, you can use some options to comply with the recommendation.
You can also install a plugin with a GZIP compression feature. WP Rocket is a good choice if you don’t mind using a paid plugin.
You can also choose to compress the text on your website manually. This can be done by editing your .htaccess files, but doing this is risky, so be sure to create a recent backup file first.
8. Avoid Multiple 301 Redirect Chains
301 redirects are used to move a user from one URL to another and are used when a page is deleted or moved. Although using redirects by itself isn’t a bad practice, they can add to page loading time and bog down a website page load. When a page has too many redirects in a sequence, it is recommended that you fix it to improve the Google PageSpeed score. The only way to fix this is by only using redirects when absolutely necessary.
9. Serve Static Assets With An Efficient Caching Policy
Google PageSpeed Insights shows this recommendation as a browser caching warning. You can implement caching through WordPress plugins. However, some hosting providers enable caching via their servers as well.
Check if your hosting provider enables caching through their servers. After enabling caching, you should check the efficiency of your caching policy. Browsers must clear their cache periodically and refresh them with new updates.
Google PageSpeed Insights and Prerender
With Prerender, your website will be optimized to score as high as possible on every speed test. Prerender is there to help you improve your search rankings first, but our tool also offers many page speed optimization opportunities, which give you an edge in Google’s algorithm. Using our services will enhance your website’s core vitals and help you interact with users effectively.
To stay ahead of the game, create a free account and get your website running at its peak.

Google PageSpeed Optimization FAQs
What Actions Can I Take To Improve My Google PageSpeed Score?
To improve your score, focus on key optimizations like compressing images, minifying CSS and JavaScript, enabling browser caching, using a Content Delivery Network (CDN), and implementing lazy loading for images and videos. For JavaScript-heavy sites, prerendering tools like Prerender.io can significantly enhance performance by serving pre-rendered HTML to users and search engines.
How Do Google PageSpeed Insights Metrics Compare to Other Testing Tools?
Google PageSpeed Insights assesses user experience by focusing on Core Web Vitals—loading (LCP), Interactivity (FID), and Visual Stability (CLS). Other tools, like GTmetrix and WebPageTest, offer more granular insights, including server response times, waterfall charts, and global testing. While all tools highlight speed issues, PageSpeed Insights emphasizes metrics that affect SEO rankings.
Can I Measure the Impact of My Changes on Page Speed Over Time?
Yes, you can measure and track the impact of your optimizations using several tools and metrics.
- Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTMetrix, or WebPageTest to test your website before and after implementing changes.
- Monitor Core Web Vitals (LCP, FID, CLS) to assess loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability.
- Use Google Search Console to view Core Web Vitals reports and track real-world user performance.
Faster page speed not only improves user experience but also directly boosts your SEO performance. Google considers speed a key ranking factor, so improvements can lead to higher search rankings, lower bounce rates, and better crawl efficiency. By regularly checking your site’s metrics and tracking organic traffic trends through tools like Search Console, you can clearly measure the results of your efforts over time.
Can Prerender.io Improve My PageSpeed Insights Scores?
Yes, Prerender has helped many brands improve their PageSpeed scores. Pre-rendering your JavaScript content with a solution like Prerender.io can have other benefits, too, such as:
- Faster crawling and indexing
- Optimized previews when you share links
- Structured data enhancement in SERPs
- Increasing your traffic
- And mitigating sudden drops in traffic
Ready to see how Prerender.io works for your website? Create a free account today.
