Prerender.io is an automatic fix for your JavaScript SEO problems, helping you get found wherever your audience searches: Google, ChatGPT, Reddit, and more. Better rendering means faster indexing, improved AI visibility, more traffic, and greater revenue potential.




900+ users signed up this month
These JavaScript SEO challenges directly impact your website’s visibility — ultimately limiting how well you reach your audience.
Average results from our thousands of clients.
Better AI SEO. Stronger site performance. Optimized social media link previews. After integrating, you’ll find that fixing your JavaScript rendering issues has a host of knock-on benefits.
AI crawlers won’t execute JavaScript. Without a rendering solution like Prerender.io, your site’s important information may not show up in AI search results at all.
Prerender.io solves this by converting your pages to HTML, an easier format for crawlers to process. We’ve found that this improves your AI search visibility by up to 100%, helping you get found by customers faster in LLMs like ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, and more.

Join thousands of developers, ecommerce brands, marketers, and agencies worldwide who have improved their SEO with Prerender.io.
Before Prerender.io, our AngularJS single-page app faced indexing issues. Prerender’s easy integration quickly led to thousands of our pages being crawled and indexed, boosting our organic traffic significantly. Their responsive support was a bonus!
I saw value almost immediately – within about a week. I could see the uptick in Google crawling activity right after implementing Prerender, and the social media previews started working properly. Those were both immediate wins that I really valued.
Enhancing the Pagespeed Insights (PSI) score for my React website was a challenge. Fortunately, I found Prerender. Their easy setup required no additional development efforts… I was elated to see my PSI score turn green!
Indexing is really fast thanks to Prerender. At this point, the indexing is on 10k pages per day. For us, that’s perfect.
We were serving Google fully rendered pages across 5700+ URLs per month in no time.
We definitely saw an uptick in search… It was literally within hours of implementation, and our team was like, ‘Oh, problems solved.’
Not every site needs a solution like ours. Try our free ROI Calculator and Site Audit Tool for clear insights on how we can help.
See your extra revenue potential by fixing your technical SEO issues.
Get clear insights into your site’s performance with a report in minutes.
Prerender.io works behind the scenes to improve search visibility for both SEO and AEO, leaving you free to focus on other work. Watch our quick explainer video to see.
Connect your website to Prerender.io. Learn more about our integration setup.
When a search crawler requests a page, your server pings us. If it has never been rendered, Prerender.io renders, feeds it to the bots, and saves it in cache.
Once the page is cached, we serve the cache to search, social media, and AI crawlers in the future. This speeds up indexing and boosts PageSpeed performance.
Your pages now load lightning-fast for search bots and AI crawlers, so you can seamlessly get found by your customers on any search channel.
Yes! We render websites with popular JavaScript frameworks.






Prerender.io is your solution to JavaScript SEO challenges. We speed up the process of serving rendered content to bots and search crawlers. This helps search engines properly crawl and index your pages, improves your page speed and can boost your SEO. Watch our short explainer video or take a product tour.
Yes! We seamlessly render sites with all popular JavaScript frameworks. Find all necessary information for developers here.
Prerender.io helps make your content accessible to all crawlers—including AI ones. Currently, major AI crawlers can’t execute JavaScript, meaning that your important information might be completely invisible to them. Prerender makes your content visible to AI crawlers by converting your JavaScript-heavy pages into easy-to-read HTML. That way, you can show up in answers from ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, and more.
Nope! We’re proudly a user-friendly, setup and go platform. Prerender fits into any modern tech stack, regardless of your JavaScript framework or backend technologies. No need for code rewrites, setup changes, or ongoing maintenance after integration.
Better crawling. Faster indexing. More traffic. Greater revenue potential. Create your free account to see the impact firsthand.
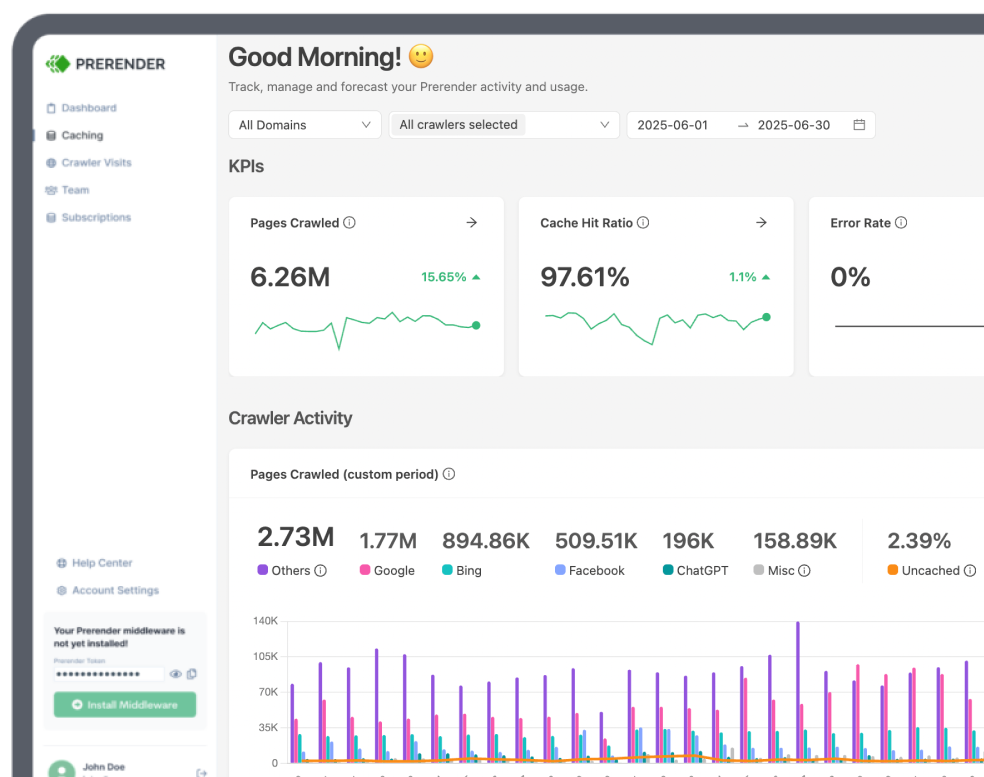
Stay up to date with the latest and most effective SEO, AEO, and LLMO optimization strategies, stats, and guides.
Calculate your revenue potential with a free ROI tool.
Get answers to your questions with video tutorials on YouTube.