Angular vs. React has become a central debate in modern web development, especially when considering SEO and GEO capabilities. JavaScript frameworks have rapidly transformed the way websites are built, and two of the most widely adopted options are Angular and React. These frameworks differ significantly in structure and purpose.
Angular is a comprehensive, enterprise-level solution, ideal for large-scale applications. React, along with React Native, is lean, flexible, and built to deliver fast, interactive user interfaces. Despite their differences, both are widely used by major companies and remain in high demand. But which one offers better performance, ease of development, and stronger SEO potential?
In this guide, we’ll compare Angular vs. React in terms of performance, popularity, and their suitability for SEO and GEO strategies.
Angular and React Compared: Summary of Their Pros and Cons
Comparison of Angular and React based on their SEO support, overall performance, learning curve, best use cases, and more.
| Aspect | Angular | React |
| Framework type | Full-stack, opinionated framework (MVC, real DOM, built-in DI, CLI tooling) | UI library focused on the view layer; relies on external libraries for routing/state management |
| SEO friendliness (out of the box) | Challenged by real DOM rendering, deep-link handling & inconsistent URLs. Needs SSR/prerendering solution for the content to rank well. | Faster initial rendering via virtual DOM, but still JavaScript-heavy. Also benefits from content prerendering/SSR treatment. |
| Performance | Heavier bundle and two-way binding leads to slower updates; meaning: ahead-of-time compilation helps, but still trails React. | Lightweight core and virtual DOM leads to one-way binding; meaning: snappier UI and better Core Web Vitals |
| Learning curve / DX | Steep: large API surface and frequent updates; shines with robust documents and enterprise support. | Gentler: minimal API, quick setup; but fast ecosystem churn requires ongoing learning |
| Content SSR / prerender options | Angular Universal or a service like Prerender.io | Next.js, Razzle, or Prerender.io for dynamic rendering |
| Best use cases | Enterprise-grade, large-team apps needing consistent delivery and long-term support (e.g., Nike and Forbes websites) | High-engagement SPAs, startups, and interactive UIs where speed and flexibility matter (e.g., Netflix and Airbnb websites) |
Angular vs. React for Modern Web Apps: Overall Performance Comparison
Angular is one of the most widely used technologies used by many JS developers. It’s an open-source JavaScript framework built and maintained by Google.
It’s known for its out-of-the-box functionality and for being highly efficient and powerful. It uses a real DOM in programming, and operates with a Model, View, Controller (MVC) structure, which splits an application into three components to make for easier testing.
Angular is used by top brands like Forbes, Sony, Nike, and UpWork.
React, meanwhile, is a more versatile technology built and maintained by Facebook. It was intended to build UI elements, but it’s also used to build full-grown websites and applications with the help of external libraries and plugins.
React is known for its numerous use cases and applications, as well as for being easy to learn and use. It offers a quick development cycle, and gives websites high performance capabilities. It’s used by startups and online-based services like Netflix, AirBnB, Uber and Instagram.
First we’ll get into how they compare in terms of mobile friendliness, performance, DOM, data-binding, learning curve and community acceptance.
Mobile Friendliness
Both Angular and React can be used to build mobile applications. Angular builds mobile apps using Iconic 2 as well as its native script. React needs to use React native, next.js and React SketchApp to do so.
Either framework would work for developing mobile apps, however React is the better option in terms of ease of development and app performance. The components that Angular uses makes it take extra time to load on mobile devices.
Point goes to React and React Native.
Functionality
Angular has more-out-of-the-box functionality – development teams can begin working with it right away without the need for any external plugins or libraries.
One of Angular’s strong-suits is that it supports dependency injection – a programming technique that decouples components from their classes, meaning that classes aren’t dependent on each other. This creates better performance on mobile devices.
React, meanwhile, requires multiple plugins and libraries before it can really become useful. Some of those include:
- Redux: A state container used to accelerate the work of React in large apps
- Babel: a transcompiler used to convert older JSX into JavaScript that can be understood by browsers
- React Router: React’s standard URL coding library
Angular has more functionality and is a more self-contained framework than React.
DOM vs. vDOM
One of the standard fixtures of web development is the use of a Document Object Model (DOM). DOM is a programming interface used for HTML documents.
Angular uses a traditional, real DOM. That means that it updates the whole tree structure of your code even if the changes take place in only one element. This makes apps slower and less efficient.
React, meanwhile, uses a virtual DOM – which tracks changes and only updates specific elements without changing any other parts of the tree. It’s considered to be faster than using a real DOM.
Data-Binding
Data binding is the process of synchronizing data between the model and view. There are two basic implementations of data-binding: one-directional and two-directional.
Angular uses two-way data binding to connect the DOM values to the model data. This makes it simpler to work with but also has a negative impact on performance – it makes it slower when the app deals with lots of data requests.
React uses one-way data binding – which doesn’t allow child elements to affect the parent elements when they’re updated. This makes code more stable and easier to debug.
Learning Curve
Angular is a difficult framework to learn and to implement. Not only that but it’s constantly being updated and added-on to, which requires Angular developers to keep on their toes and constantly be plugged into the Angular community to see what’s changed.
The Angular framework contains a huge library, and learning the concepts necessary to make it work takes much more time.
React, on the other hand, is a minimalistic framework that is much friendlier to newcomers to the language and is much easier to learn.
Community Acceptance
Angular has a bad reputation because of the poor performance and stability of Angular 1.0, and is to this day often dismissed by developers as being needlessly complicated. In its favor however, Google takes pains to make constant improvements to the framework and offer long-term support. Angular also balances out its difficulty and learning curve with robust documentation.
React, meanwhile, has wider community support and is generally more popular in online web development communities. It’s also constantly changing and requires developers to continually relearn the network.
Angular vs. React: Which JavaScript Framework is More Popular?
Angular and React are both widely used across many industries and by many of the world’s most recognizable brands. But which one do web developers themselves enjoy working with more?
It’s worth pointing out that the topic “React” historically has trended over “Angular” on Google since at least 2015.
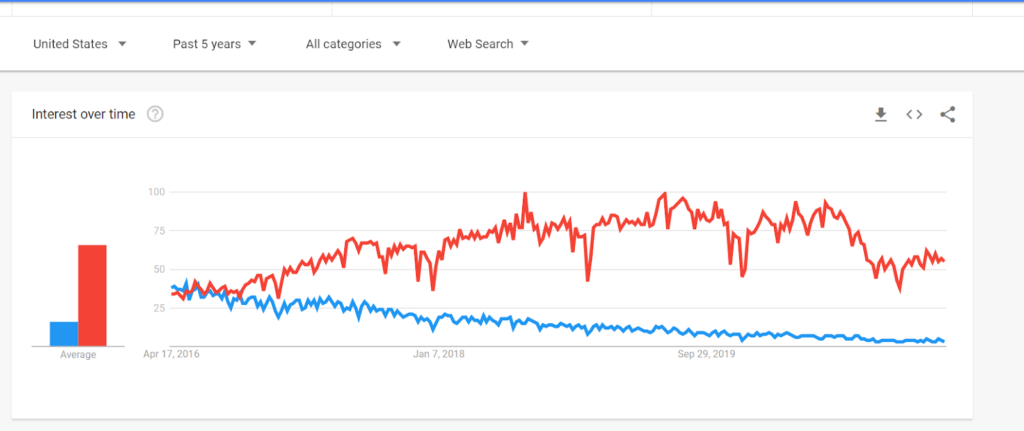
However, this is a tricky metric to judge by because the word “React” is a generic, commonly-used action verb as well as a noun. To really get to the bottom of it we need to dig a little deeper.
A 2024 survey hosted by Stack Overflow, the web developer community forum, listed React.js as the most popular web framework among professional developers, with 39.5% usage, ahead of Angular at 17.1%, out of over 65,000 responses.
In terms of performance, both Angular and React have their strengths, but React slightly edges Angular. A recent performance comparison using PageSpeed Insights revealed that React had the fastest Speed Index at 0.8s, with Angular taking second place at 1.2s.
React’s virtual DOM and efficient diff algorithm contribute to its performance advantages, especially in applications with frequent dynamic content updates. Angular’s performance is still competitive, particularly with the recent advent of the Ivy renderer, which significantly improves rendering times and bundle sizes.
Angular vs. React for AEO and AI Search: What You Need to Know
As AI-powered search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) become more prominent, the way these frameworks render content plays a critical role in discoverability.
React’s flexibility with pre-rendering and static generation makes it easier to serve AI crawlers clean, digestible HTML, which can boost visibility in AI-generated answers. Angular, while powerful, may require more configuration or third-party tools to ensure content is accessible to AI-driven search experiences. We’ll dive deeper into this topic later.
Is Angular or React Better for Your Website’s SEO?
Angular and React were made to fulfill different needs. React and React Native are libraries that deal with coding in views, and Angular is a full-fledged framework that works with a model-view-controller model.
Angular trails React in popularity but is steadily gaining a foothold, particularly in the corporate world. Its standardization and long-term support make it well-suited for bigger teams and projects.
Angular has more out-of-the-box functionality. It requires no additional libraries or plugins to work, and you can start building your web app with it right away. It’s good if you need to build a minimum viable product and start development immediately. Angular also has some SEO limitations that require third-party plugins to overcome.
React, meanwhile, is simpler and lighter. It takes less time to start working on a project, and it has a faster development cycle. React is arguably the most SEO friendly of the two frameworks because of its pagespeed performance enhancements and its Virtual DOM work environment. The tradeoff is that React requires a longer initial setup process because it’s not fully functional on its own, and requires plugins and libraries to be useful.
Angular and How it Supports SEO
Angular is robust and capable of making powerful applications, but is it an SEO-friendly JavaScript framework? Here are some of the SEO problems you might encounter when working with Angular:
- Real DOM: Angular renders JavaScript in a real DOM environment. Google looks at the initial HTML parse before it looks at the content executed in JavaScript.
- Deep Links: The deep links created in Angular web applications are hard to get indexed. There are ways to do it but they’re difficult and time-consuming
- Inconsistent URLs: Requests for new content are populated with asynchronous JavaScript and AJAX calls. The fact that no new page is loaded that the address in the URL bar doesn’t match the content on the screen.
React and How it Supports SEO
React is the most popular JavaScript framework and React-based apps come with some nifty performance enhancements which are nice to have from an SEO standpoint. However, you can expect some of the following issues when working with react:
- Long delays: Google indexes most web pages with a two-wave indexing system: crawl, and index. With SPAs (single-page applications) built with React, the process is slower and more complex.
- Limited Crawling Budget: JavaScript pages take longer for Googlebot to fetch and parse. If it takes too long for Google to render your page, it will simply leave without indexing your content.
- Lack of Dynamic SEO Tags: When it comes to React SPAs, there’s a good chance that your SEO meta-tags like you title tags and meta-descriptions won’t be set correctly and won’t make it through the indexing process
How to Make Angular and React Sites AI Search and GEO Ready
Option 1: Adopt Prerender.io to Render Your JavaScript Content
For Angular and React apps, Prerender.io is one of the most effective solutions to ensure your content is both SEO- and AEO-friendly. It works by generating static HTML snapshots of your dynamic pages, allowing search engine bots and AI crawlers to instantly access your content without executing JavaScript. This is especially critical for AI-based engines like ChatGPT and Google SGE that prioritize fast-loading, structured content to power their direct answers.
Unlike traditional SEO tools, Prerender bridges the gap between modern JavaScript frameworks and the needs of AI search engines. It ensures your metadata, headings, and body content are fully exposed to crawlers—even if your frontend relies heavily on client-side rendering. The result? Better rankings in search engines and higher chances of being featured in AI-generated summaries and answers.
If you’re building with Angular or React and care about visibility in the age of AI, Prerender.io isn’t optional—it’s foundational.
Watch this video to learn more about how Prerender.io works.
Option 2: Server-Side Rendering (SSR)
Another route to AEO readiness is server-side rendering (SSR). SSR allows your Angular or React app to render content on the server and deliver a fully-formed HTML document to the client. This improves load times, enhances crawlability, and aligns well with how AI engines process content.
That said, building an in-house SSR can be expensive. The initial investment can reach around $120,000 and months of infrastructure implementation. In contrast, Prerender.io is a plug-and-play solution. Installing it requires a couple of hours, and in a few weeks, you can start seeing the SEO and AEO improvement to your Angular or React-based websites.
Learn more about the financial and technical burden of adopting in-house SSR vs. Prerender.io.
How to Enable SSR in Angular
Angular defaults to client-side rendering and requires a library called Angular Universal to render JavaScript content on the server rather than on the browser. This enables it to give static HTML application pages to search engine bots for seamless crawling and indexation. It also renders more quickly, letting users interact with the webpage sooner and enhancing user experience.
1. Create your Web App
First, check to make sure you have the latest Angular CLI – 9 or greater:
ng –version
If your CLI version is less than 9, you can upgrade it to the latest version:
npm i -g @angular/cli
Then, initiate your web app:
cd angular-SSR-Demo
npm start
2. Install Angular Universal
To create your server-side app module, run app.server.module.ts, then run the following command:
ng add @nguniversal/express-engine
Open a terminal from your app directory, and run the following command:
$ ng add @nguniversal/express-engine –clientProject {{ name of your project }}
3. Configure your Angular App for SSR, and Test to Make Sure It’s Working
Run Angular Universal from @nguniversal, and add an express server to your project.
“@angular/platform-server”: “~10.0.9”,
“@nguniversal/express-engine”: “^10.0.0-rc.1”,
“express”: “^4.15.2”,
npm run dev:ssr
With this in place, you can now test to make sure it’s working by emulating different kinds of networks.
- Open the Chrome Dev Tools and go to the Network tab.
- Find the Network Throttling dropdown on the far right of the menu bar.
- Try one of the “3G” speeds.
The app should be performing well on all network types.

How to Enable SSR for React
Next, we’ll get into how to enable server-side rendering for React.
1. Choose a framework
First, choose a framework with which to use in conjunction with React. Your options are either Next.JS or Razzle for this one.
2.Create your React App
Run the following command:
npm init –yes
Then, install all the dependencies you need:
npm install
3. Create the Server
This is the code that enables SSR.
import React from ‘react’;import { renderToString } from ‘react-dom/server’;import { Provider } from ‘react-redux’;import configureStore from ‘./redux/configureStore’;import App from ‘./components/app’;
module.exports = function render(initialState) {// Model the initial state
const store = configureStore(initialState);let content = renderToString(
Configure the app for the client-side
We create the pure client-side app as follows:
import React from 'react';
import { render } from 'react-dom';
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
import configureStore from './redux/configureStore';
import App from './components/app';
const store = configureStore();
render(
<Provider store={store} ><App /></Provider>,
document.querySelector('#app')
);
Then make sure that the content is the same on the server as on the client-side:
import React from 'react';
import { hydrate } from 'react-dom';
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
import configureStore from './redux/configureStore';
import App from './components/app';
const state = window.__STATE__;
delete window.__STATE__;
const store = configureStore(state);
hydrate(
<Provider store={store} ><App /></Provider>,
document.querySelector('#app')
);
And finally:
npm run build && npm run start

Boosting SEO and GEO with Angular or React: Which Delivers More?
Angular and React are two of the most widely-used web development frameworks on the internet. Each of them have their own advantages and drawbacks, and each of them have their own unique limitations when it comes to optimizing for search engines.
A comparison between the two shows:
- Angular has more out-of-the-box functionality and is meant for more powerful and complex web applications
- React has a lower barrier-to-entry and has performance benefits which are advantageous to SEO
- Use Angular Universal to configure your Angular web app for SSR, and use Next.JS or Razzle for React.
Angular vs. React FAQs: SEO, Performance, and Technical Considerations
How Do Single-Page Applications (SPAs) Built with Angular or React Affect SEO?
SPAs built with Angular or React can pose challenges for SEO because:
- They often use client-side routing, which can make it difficult for search engines to discover and index all pages.
- Content is typically loaded dynamically, which some search engine crawlers might not fully render.
- To mitigate these issues, implement server-side rendering and/or prerendering solutions, and ensure proper use of the History API for routing.
Can I Improve the SEO of my Existing Angular or React Application Without Completely Rebuilding It?
Yes, you can improve the SEO of your existing Angular or React application without a complete rebuild. Some strategies include:
- Implementing server-side rendering or prerendering
- Optimizing your content and metadata
- Improving page load speed
- Ensuring proper use of semantic HTML
- Implementing proper URL structures and internal linking
These improvements can often be implemented incrementally without requiring a full application redesign. Using a tool like Prerender.io can help with almost all of the above. Get started with 1,000 renders for free.