Online recruitment sites are a $17.4B industry that keeps growing 5-10% year-over-year (YoY), creating many opportunities for new players to enter the game and more competition for your job board site.
To stay relevant, you need to ensure companies and job seekers choose your platform over hundreds of choices. In other words, you need to be where people go to find jobs, which starts with Google.
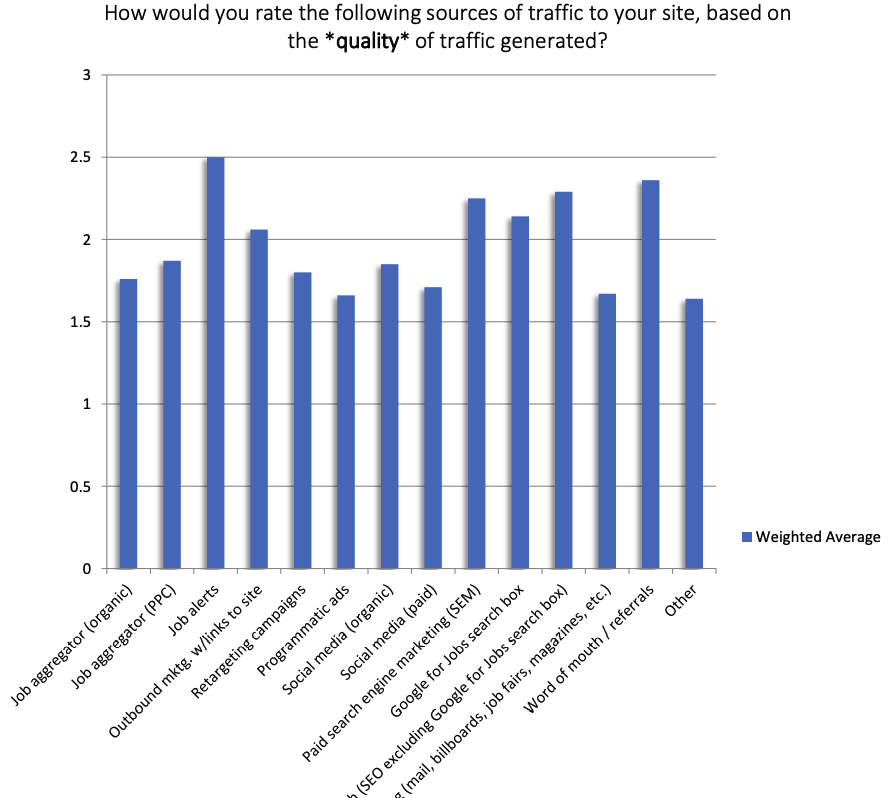
According to Zippia: “80% of all job searches are done online as of 2022,” but more impressive is how much traffic comes directly from organic sources. In their 2022-23 Global Recruiting Site Trends Survey, conducted since 2010, Job Board Doctor listed SEO (organic search results) and Google for jobs as two of the highest sources of traffic for job boards.
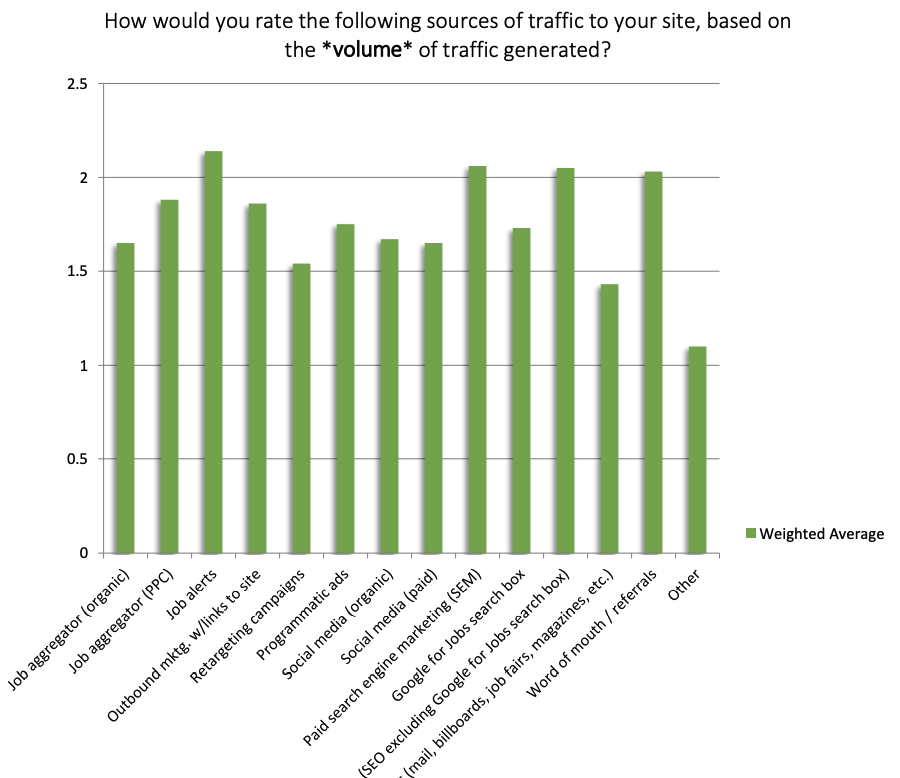
These two channels not just bring the most visitors but also the highest converting traffic, only surpass by word of mouth/referrals and job alerts:
Increasing your visibility in search engines guarantees a steady flow of job seekers that are ready to take action and jump-start their next opportunity. This makes your site extremely desirable to companies, creating a positive loop that’ll help you grow your business sustainably. To help you begin this path in the right direction, let’s explore all major challenges, nuances, and strategies you’ll need to focus on:
What Makes Job Board SEO Unique?
Like any other site, job boards must follow Google’s guidelines, implement SEO best practices to ensure they are crawled and indexed properly and efficiently, and optimize their pages to increase the chances of high rankings on search engine results pages (SERPs). However, job boards are also more complex than your average website, and have many moving parts requiring a different approach to succeed.
Here are four characteristics that set job board SEO apart:
1. High Number of URLs
Even the smallest job boards have a couple of hundred URLs, and hundreds more are added weekly to their catalog. This ever-growing number of pages makes manual optimizations hard to sustain in the long run, and impossible to scale. That being said, in most cases, job boards actually handle thousands of pages every month. Most of them are job listings dynamically generated by employers and recruiters.
This requires higher automation and planning to be able to optimize every page without increased overhead or burnout for the team.
2. Ever-Changing Job Listings
Job listings are not just getting added but also removed. This type of content is very particular, as these are ephemeral by design. The posts are meant to be filled and deleted once the vacancy is closed.
As Tomas Laurinavicius (Growth Manager at saas.group and Co-Founder of Best Writing, a job board for content writers) puts it: “SEO generally works better for evergreen content. The job board’s primary content is the opposite. Jobs expire, and even if you rank for a specific job post, there’s a big chance that once it appears on Google search results, the position will be filled, expired, or entirely removed.”
Because of this, you need to find ways to optimize job listings without depending on them completely for your organic traffic, creating a very unique paradigm most other types of websites don’t experience.
3. Handling JavaScript and Dynamic Content
A massive number of URLs also requires a lot of automation. In addition to rules on how to generate this content, you also need to think about how to display it correctly. The latter usually comes down to using JavaScript to show job listings dynamically, creating filtering options to make navigation easy for customers, and much more. However, JavaScript also opens the door to SEO issues. Your team will need to think about factors like rendering, PageSpeed implications, and JS optimization at a greater scale.
4. Google Treats Job Listings Differently
Most websites just need to care about showing on Google search results.
However, Google designed a specific search engine for job postings called Google For Jobs (GFJ). This is a different search list (like Google Images or Google News) and greatly impacts your job board’s traffic potential. If you remember the graph from the introduction, you noticed this channel is the seconds largest source of traffic for job boards (only surpassed by regular Google SERPs), but GFJ results are also – in most cases – shown first in the SERPs above organic “traditional” results.
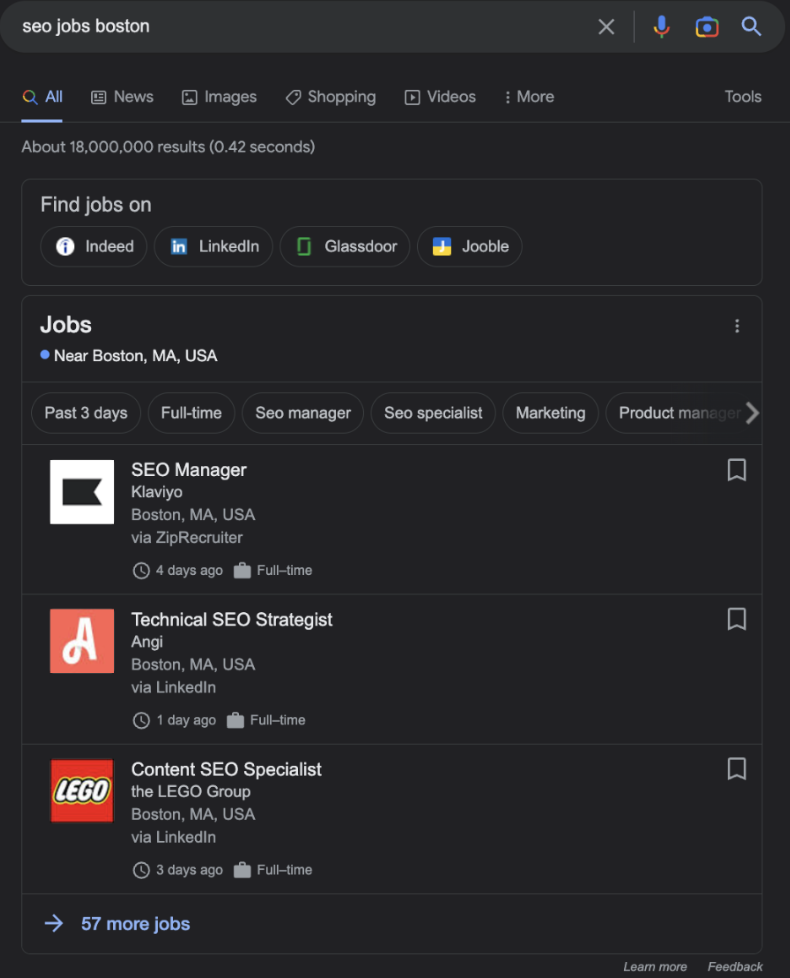
To get ahead of the competition, job boards need to optimize for Google Search and Google For Jobs and balance the traffic of job seekers and employers so there’s no shortage. Pulling this off is not easy, and it will require you to take action and invest in a collection of tasks to avoid burning your budget.
Because technical SEO is the foundation of your site, we thought it was a good idea to list these tasks going from the more technical to those related to content and, finally, some ideas for link building.
If your site is faulty, can’t be crawled efficiently, or is not optimized for indexation, then the quality of your content or number of backlinks means nothing. So it’s a good idea to fix all of these first – unless your team is big enough to work on things simultaneously.
Use Dynamic Rendering to Serve JavaScript to Search Engines
Ten to one, your website uses JavaScript to display job listings in category pages. It is also likely that you’ve implemented a JS framework like Angular, React, or Vue to build a feature-rich front-end to provide a faster and smoother user experience for job seekers – like filtering and search options.
All this is great for users but not so much for search engines.
In simple terms, search engines need to crawl your site. It is done by following every link on your pages and then categorizing each page to get added to its index. (This is the common process for static HTML sites). Now, when you get JavaScript involved, crawlers have to add an extra step to download, execute and render your JavaScript files and be able to see the content on the page instead of a blank file.
Resource: Learn how Google sees JavaScript content in detail.
This additional step takes up to 9X more resources and time, depleting your crawl budget faster. This also creates rendering problems like missing content and undiscovered links (blocking crawlers from finding subsequent pages). All this translates into low index rates and, of course, low rankings.
Although you can use rendering solutions like server-side rendering or hydration to help crawlers understand your pages, these are highly-expensive workarounds that still don’t bring the complete benefits you want for your site’s growth. Instead, we recommend you use dynamic rendering through Prerender to serve a fully functional and rendered HTML version of your pages to search engines.
Because Prerender removes the entire rendering process for search bots, it becomes possible for them to crawl your site faster. In a fraction of the time, they can find and understand your content without delays or setbacks, and index your pages correctly every time, solving JavaScript SEO from its root.
Build a Clear Site Architecture and Navigation
Now that search engines can see your pages, it’s time to get them in order. Making your website easy to navigate will help your visitors (aka job seekers) understand how to use your site to find what they need.
It also helps search bots crawl your site quicker and categorize content in relationships (groups).
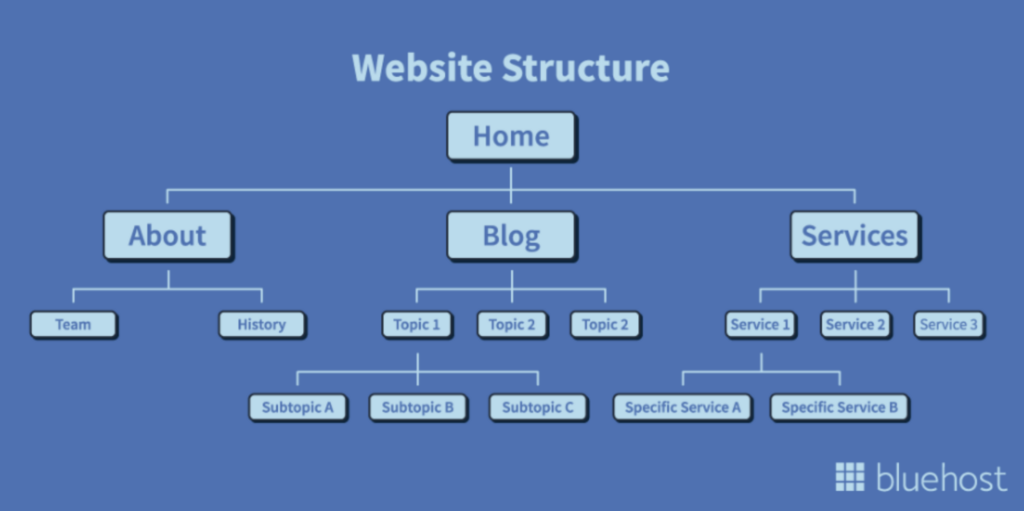
Image source: Bluehost
Well-defined groups and rules will help keep content under control and prevent issues like conflicting URLs (several pages having the same slug) or orphan pages (URLs without links connecting them to the rest of the website). For this to be effective, you must define your job listings and content categories, set clear rules on how pages will be created (URL conventions, internal links, etc.), and avoid overlap as much as possible (keyword cannibalization) to send clear signals to Google regarding what your pages are about. Note: We’ll explore how to plan and optimize your category pages in the content section.
Use the Right Internal Link Structure and Pagination
Another crucial aspect of navigation and site architecture is internal linking.
After all, your internal links are what allow users and search bots to move from page to page. Still, knowing there’s a clear difference between how people and bots can interact with your links is important.
A common mistake we see in JavaScript-based sites is the use of trigger-driven links. These are links that require some kind of interaction to trigger a JS function to take the user to the target URL.
These are a few variations of this type of link:
| <a href=”#” onclick=”alert(‘Hello, World!’)”>Click me</a> <a href=”#” onclick=”window.location.href=’https://www.example.com’“>Go to Example.com</a> <a href=”#” id=”myLink”>Click me</a> |
For Google to be able to crawl your site, stick to the traditional link structure with a complete URL within the “href” attribute:
| <a href=”https://prerender.io/blog/optimize-pagination-seo/“>Learn more about pagination and SEO</a> |
In the same line of thought, pagination should also be implemented using this structure. Because each category will have so much content, you’ll have to break it down across several pages.

Instead of using a JS pagination like infinite scrolling, it’s better to use a numbered paginated series, allowing Google to find all links fasters and providing a cleaner URL structure. Note: Although Prerender will render all links, without this structure, Googlebot won’t be able to interact with them. Why? Crawlers are programmed to find all <a> tags on every page and navigate to the URL within the “href” attribute.
Make PageSpeed a Priority
Loading your pages fast is a crucial part of the user experience.
Many studies have pointed out that PageSpeed significantly impacts conversion rates.
While pages loading in one second have a 3.05% average conversion rate, those loading in two seconds drops to 1.68%. So it’s no wonder why Google made PageSpeed a ranking factor.
To measure page performance more accurately, Google uses metrics called core web vitals (CWVs):
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- First Input Delay (FID)
Optimizing your site’s core web vitals is what’ll make you stand out from your competition, but it can be challenging. Note: Although we’ll try to give you a quick overview of where to start optimizing your CWVs, you can read our core web vitals optimization guide for an in-depth, step-by-step process.
Using these strategies will ensure better page loading scores and a smoother experience for job seekers:
- Use the width, height, and “srcset” attributes on images
By adding the width and height, you tell the browser how much space it will need to save for each image. Combining this with the “srcset” attribute for responsive images (to add variants of the image for the browser to pick the one that better fits the screen size), you’ll improve CLS scores.
| <img width=”1000″ height=”1000″ src=”puppy-1000.jpg” srcset=”puppy-1000.jpg 1000w, puppy-2000.jpg 2000w, puppy-3000.jpg 3000w” alt=”Puppy with balloons” /> |
- Optimize your images
Images are, most of the time, the biggest files on your pages, so reducing their size and improving how they load can have a big impact on your site’s loading speed.
To reduce your image sizes, you can do a couple of things:
- Compress your images using a tool like TinyJPG.
- Resizing your images so they match the size they are displayed on. If an image will be displayed as 600 x 600, there’s no need to use an 1800 x 1800 image.
- Turn all PNG images into JPEGs or, if possible, to Webpg – which is the lightest image format.
In terms of loading, there are two things you want to ensure: above-the-fold content is loaded first and avoiding off-screen images from loading all at once.
The good news is that you can do this by just lazy loading all images but the header images using the loading attribute:
| <img src=”super-happy-cat.jpg” loading=”lazy” alt=”kitty playing with some feathers” /> |
These will definitely help increase your LCP score and provide a faster experience for job seekers – especially those using mobile phones.
- Defer and prerender your JavaScript
There’s no way to go around it, JavaScript takes a toll on your site’s loading speed. There are two main characteristics of JavaScript you need to optimize first:
- JavaScript is render-blocking – When the browser finds a JS script, it’ll stop the rendering of the page from downloading and execute the JS first – this happens because JS can alter the layout and content substantially. This can leave the job seeker staring at a blank page for seconds or even minutes if your JS code isn’t well optimized.
To avoid this issue, you can use the defer attribute on all non-essential JS scripts like so:
| <script defer src=”example.js”></script> |
It will force the browser to handle this JS file last, freeing resources to render the content first.
- Search engines have limited resources – The other side of the problem with JS is that search engines don’t count with enough bandwidth to handle your dynamic content properly. Even optimizing every bit of JS, you will still get a low page performance score due to these features.
To solve this issue, it’s better to take this process out of search engines’ hands and use Prerender to serve a fully functional version of your page.
By following these two strategies, you’ll ensure higher FID scores – which people will definitely appreciate– as well as near-perfect core web vitals in general, thanks to Prerender.
Use Automation to Scale Technical Optimization
As Ané Wiese, SEO Marketing Manager at saas.group, reminds us:
“Optimizing each individual page from a pool of millions is impossible. If you want your business to scale, you must automate as much as possible – without losing quality – to make every page compliant with Google’s best practice guidelines. This will increase your chances of getting the first spots in SERPs.”
A good place to start automating is at the job listing level. Recruiters and companies will constantly create new pages, and without automation, it can easily become a spiral of low-quality content.
Add required fields during the job listing creation process to gather the information you’ll use as metadata and to help better organize the information. For example, the job title can be a great H1, while a combination of the company name and job title could be a great meta title. In the same way, you can use part of the job description as part of the meta description (or a quick description of the job.)
In addition, a combination of the job industry, company name, and title could make for a unique URL, preventing URL conflicts.
Of course, this is just an example of many different processes that could be automated for scalability.
Systems to automatically generate and update your sitemap or create redirect rules so removed job listings redirect to their main category page are a must-have to ensure your team can manage and scale your platform in the long run.
Optimize Job Listings for Google Search and Google For Jobs
Your job board’s main content, the reason people actually want to visit your site, is because of job listings, so increasing their visibility through SEO is critical, and here’s when things get a little paradoxical.
You want to have the best job posts possible, but you’re not the one writing them. Employers and recruiters are.
As mentioned in the previous section, adding required fields during the job publication process can automatically generate certain SEO elements. In particular, you want to have these elements optimized at all times:
- URL – Set a rule so the category or industry, location, company, and job title appear on the slug of the job post. A good structure could be something like: https://somejobboard.com/category-or-industry/senior-seo-new-york-company-name
- Headings – You can optimize the job listing template to add headings like “about the company” and “job description” and then use those as H2s. Also, the job title and location are a good combination for the H1 of the post.
- Meta title – You use the job title in combination with location and/or company. Think of something like: “[Company Name] is looking for [Job Title].”
- Meta description – Although you can just take an extract of the first 160 words from the job description, you could also add a required field for employers to add a summary of the role.
These optimizations will help Google understand and display your jobs correctly on search results.
Going further, you also want jobs to be featured in Google For Jobs. This adds more visibility to your jobs, and employers will expect that your website is optimized for it.
To get your pages into GFJ, Google released a specific schema markup (JobPosting structured data) that can be used specifically for job posts. Implementation is simple, just add the schema to your heading and fill the fields with your own information:
| <html> <head> <title>Software Engineer</title> <script type=”application/ld+json”> { “@context” : “https://schema.org/”, “@type” : “JobPosting”, “title” : “Software Engineer”, “description” : “<p>Google aspires to be an organization that reflects the globally diverse audience that our products and technology serve. We believe that in addition to hiring the best talent, a diversity of perspectives, ideas and cultures leads to the creation of better products and services </p>”, “identifier”: { “@type”: “PropertyValue”, “name”: “Google”, “value”: “1234567” }, “dateposted” : “2017-01-18”, “validThrough” : “2017-03-18T00:00”, “employmentType” : “CONTRACTOR”, “hiringOrganization” : { “@type” : “Organization”, “name” : “Google”, “sameAs” : “https://www.google.com”, “logo” : “https://www.example.com/images/logo.png” }, “jobLocation”: { “@type”: “Place”, “address”: { “@type”: “PostalAddress”, “streetAddress”: “1600 Amphitheatre Pkwy”, “addressLocality”: “Mountain View”, “addressRegion”: “CA”, “postalCode”: “94043”, “addressCountry”: “US” } }, “baseSalary”: { “@type”: “MonetaryAmount”, “currency”: “USD”, “value”: { “@type”: “QuantitativeValue”, “value”: 40.00, “unitText”:“HOUR” } } } </script> </head> <body> </body> </html> |
Example from Google
Just like with metadata, you can add this schema to your job post template and generate it dynamically for each listing based on the data provided by the employer.
Note: We recommend you check Google’s page on the JobPosting schema to understand their policies and find extra context on, for example, differences in the schema for remote jobs.
Jobs Inform Categories, and Categories Inform Keyword Research
Even if you can’t control every detail in job posts published on your site, you can definitely optimize the second-best thing: your landing pages. Of course, before you can do that, you need to know which categories you’ll need to create, and you can start by understanding your niche.
There are many different approaches to keyword research based on the type of job board you’re running:
- You could first catalog the most popular jobs on your site and build category pages for similar jobs and roles. For example, you can use the keyword “web developer jobs,” which has a 5k search volume, to build your landing page.
- If you have a niche job board site, you can use Best Writing’s approach and build landing pages for the different variants of the role.
- You can also build landing pages per industry, like “finance jobs” or “IT jobs.”
Once you know which categories to build, you can use the primary keyword in the following elements:
- URL – If your main keyword is “finance jobs in New York,” add it to the slug of the landing page like https://somejobboard.com/finance-jobs-new-york.
- Metadata – Adding your keyword in the meta title and description will signal Google the main topic of your page. Plus, having the keyword on these elements would also entice searchers to click your link in the SERPs.
- Headings – Add your main keyword as the H1 and use related terms as H2s.
A common practice for these types of landing pages that have been successful in other industries, like eCommerce, is adding an FAQ at the bottom of the page. You can use the “People also ask” box for inspiration and keyword ideas.
Create and Scale a Blog
We’ve talked a lot about job listings and category pages, but these are not the only way to attract traffic to your platform. In fact, Glassdoor brings 210k visitors per month through its blog content.
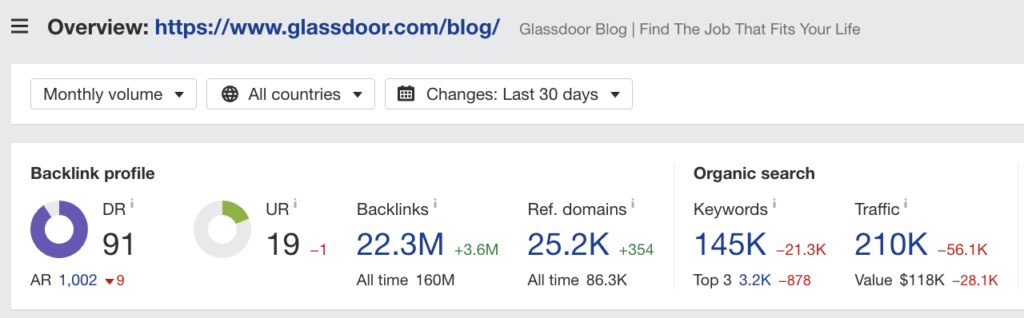
Creating content will help you increase topic relevance and expertise in Google’s eyes (helping your landing pages and job posts rank higher) and attract both job seekers and employers.
The most important thing to keep in mind when developing your content strategy is search intent. You don’t want to create content about any topic around every available job on your platform.
Instead, you have to think like your audience and ask yourself: what a person looking a job/hiring in this field would search for?
Also, your site produces a massive amount of job data. You can leverage this information to create unique pieces of content no other platform can.
For inspiration, here are some content ideas worth exploring:
- Share Salary Statistics
When professionals are looking for new roles or to jump into a new field, salary is one of the first aspects they look for. By using the salary data from the job listings on your site, you can provide unique insides on salary ranges for different roles, locations, and industries.
Here are a couple of examples:
- How much does a Software Developer make in Helsinki, Finland? (Glassdoor)
- GAME Developer Salary (ZipRecruiter)
- Interview Questions and Process Pages
The interview process can be brutal, so job seekers are always looking for the latest tips and strategies to prepare for the big day.
You can create different guides on questions employers tend to make for particular roles or tips to negotiate salary. These pages can also attract recruiters looking to learn what questions to ask during their interviews.
Here are a couple of examples:
- 20 Customer Success Interview Questions to Ask Your Next Candidate (HubSpot)
- Administrative Assistant Interview Questions (Indeed)
- List Companies Hiring Right Now
Listicles of companies hiring for specific positions are both useful and searchable – also, you might want to update this page every quarter (or even monthly) to stay relevant.
Here are a couple of examples:
- 25 Companies Hiring for Remote, Work-From-Home Jobs Right Now (FlexJobs)
- Top Companies Hiring Web Developers in 2022 (CareerKarma)
- Job Description Templates
People searching for these types of templates are most likely thinking about publishing a job opening (recruiters and employers), so attracting traffic from these keywords is very relevant and more likely to convert.
Some examples:
- Account Manager job description (Workable)
- Marketing Manager Job Description: Top Duties and Qualifications (Indeed)
Leverage Job Data for Link Building
As mentioned above, your job board platform produces unique and interesting data that can be used to write data-driven pieces that can easily build a lot of organic backlinks.
Here are some ideas to explore:
- Create industry and job reports – creating reports that show job market shifts, salary changes over time, or even job trends like in-demand roles are hard to come by. Writers can use these statistics to complement their ideas, and, of course, they’ll link to the source.
- Build shareable assets like infographics – infographics are great for explaining complex information in an engaging way, but they also require design skills or monetary investment. Other websites can use your infographics to prove a point or showcase some data that supports their claims.
- Pith your platform as a resource for universities – some universities can be interested in using your platform to help students find jobs. If you play your cards well, you can get highly valuable backlinks as well as a source of job seekers.
- Do guest blogging on HR sites – you can use your unique knowledge to write about hiring practices, job trends, etc., on recruitment and human resource websites.
- Use HARO to build backlinks to your homepage – Help a Report Out (HARO) is a platform to connect journalists (and writers) with sources. Basically, they request certain information, and you get a daily email with all pitching opportunities. If your answer gets picked, they’ll quote you and give you a backlink (usually to your homepage).
Backlinks are the main signal Google uses for trust. Every backlink is like a vote in your favor, and as you can imagine, the bigger and more trustworthy the site that links to you is, the stronger the endorsement.
That said, stay away from practices like link exchanges or directly buying backlinks, which are frowned upon by Google. If they identify a pattern in your link building, they can penalize your site severely.
SEO is a competitive and multidisciplinary channel, full of challenges but with the potential to bring big returns. For job boards, being findable through Google is a requisite to stay afloat because if job seekers can’t find your site, employers won’t be interested in using it either.
We hope that these strategies help you in your journey. We know it’s a lot to process in one sit, so please refer to this guide as you go along, and implement each strategy step by step. Just remember that in SEO, consistency is key. Treat it as a marathon instead of a sprint, and you’ll see results soon!