Have you ever been lost in an online store trying to find a product? That’s the same experience search engine bots have when crawling ecommerce websites with poor site structures.
Ecommerce websites typically have thousands of product pages that need to be logically structured. Without proper organization, it becomes difficult for Google to crawl and understand your product pages and their SEO elements.
So, what’s the best way to structure your ecommerce website? This Prerender.io blog will provide you with the best practices for structuring your eCommerce website and setting the right site navigation type to meet Google’s requirements.
But first, let’s cover the basics of eCommerce crawling and indexing.
What Makes Ecommerce Websites Prone to Crawling and Indexing Issues?
Compared to “normal” websites, ecommerce sites have unique characteristics that often prevent Google from crawling and indexing them effectively. Some of them are:
- Most ecommerce pages are built with a JavaScript framework, which is notoriously difficult and slow to index. This blog explains the challenges search engines face when processing JS content.
- They host thousands of product pages that are rapidly and dynamically updated (e.g., product stocks, prices, and customer reviews).
- They have a complex site structure due to the various product categories and types.
- They are prone to duplicate content.
If not specifically addressed, these issues can significantly impact your website’s visibility, potentially leading to missed traffic and sales.
How Google Crawls and Indexes Ecommerce Websites
Principally, how Google crawls and indexes ecommerce product pages is the same as processing “normal” pages. They still look at the content quality and relevance, as well as the on-page SEO (e.g., metadata) and technical SEO health (e.g., page speed and internal linking).
Related: Discover some important Google ranking factors to ensure your product pages land at the top SERPs here.
That said, some key factors are emphasized when crawling and indexing ecommerce product pages, as explained below.
1. Product information
To understand an ecommerce product page, Google “reads” the product information. This includes the product page title, descriptions, and images. When they find the content to be too similar (or duplicated), it damages your content quality scores and will likely deprioritize the page from being indexed.
2. Mobile-first indexing
With the surge in mobile shopping, Google prioritizes ecommerce sites that deliver a seamless mobile user experience through responsive design. Optimizing your site for mobile is no longer optional, it’s essential.
Pro tip: Follow these 8 easy steps to improve your ecommerce site mobile user experience.
3. Product reviews
Positive reviews and high ratings on your product pages and online store can build trust with your customers and Google. Stellar reviews signal Google that your site is trustworthy and provides a good user experience.
4. Website structure
When crawling a website, Google follows its structure to trace the link and understand its page roles and information. The cleaner and more logical your ecommerce site structure is, the easier and more accurate Google processes it.
6 Tips to Enhance How Google Understands of Your Ecommerce Website Structure
We now know that a well-organized site structure is crucial for search engines to index your ecommerce store effectively. This, in turn, can significantly boost your site’s visibility and ranking potential. Here are 6 best practices to improve your site’s organization and maximize your sales potential.
1. Use a Logical Information Architecture (IA) and Internal Navigation
A logical information architecture is essential to help Google understand your site structure because it guides customers and crawlers to the right places.
When you hierarchically structure your categories, subcategories, and individual product pages, Google receives clear signals about how all the content fits together. For instance, you wouldn’t want ‘shoes’ and ‘electronics’ lumped together under one umbrella category, but you’ll want to group various types of products in the same category hierarchically. For example, ‘Women > Shoes > Basketball Shoes’ and ‘Women > Shoes > Running Shoes’.
To accomplish this, optimize your internal navigation system. Internal navigation allows you to link pages A and B, enabling Google to understand that these two pages are related. This also helps Google crawl deeper pages within the categories, helping the overall indexing process.
This guide will tell you more about internal navigation and how to implement it properly.
2. Amp Up Your PageSpeed
Fast page speed can lead to a faster and more thorough indexing of the site’s structure and content. Slow page speed, on the other hand, can negatively impact Google’s ability to understand your ecommerce product pages. It also results in poor UX and high bounce rates since users quickly abandon slow sites.
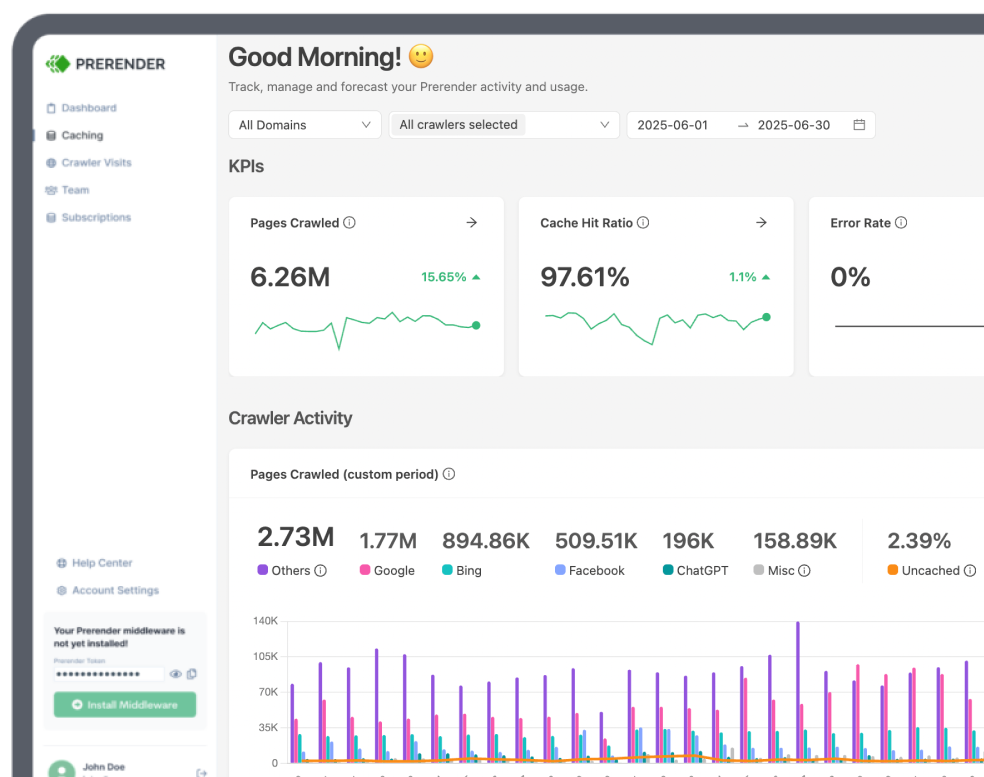
For large ecommerce sites, adopting an SEO rendering strategy focused on optimizing server response time (SRT) can significantly enhance SEO performance. Prerender—an enterprise SEO rendering ecommerce solution—is a highly recommended tool for handling this job.
Prerender’s dynamic rendering empowers your online store to enjoy an SRT under 50 milliseconds. And since your server performance is now blazing fast, it will take Google a shorter time to crawl and process your pages, leading to higher and more thorough indexed pages. If you want to experience this on your ecommerce site, get started with Prerender today.
3. Implement Proper URL Structures
At first glance, URLs may seem like nothing more than a web address for locating a page, but they’re essential in structuring your site for search engine optimization. URLs or links create a clear path for Google to understand your site’s page content and hierarchy, leading to improved site crawling, indexing, and ranking.
Some of the best practices in creating a proper URL structure are:
- Use descriptive keywords in the URL paths, such as ‘domain.com/category/subcategory/product-name’. This tells Google exactly what the page is about.
- Keep the URL simple, short, and clean.
- Use URL subdirectories instead of query parameters where possible. For example, ‘category/dresses/’ rather than ‘category?type=dresses’.
- Keep URLs consistent across the site architecture. Be careful not to mix parameters and subdirectories on different pages.
- Hyphens ‘-’ are more readable and should be used to separate words instead of underscores ‘_’.
4. Optimize the Product Pages’s Meta Tags
Though invisible on your webpage, meta tags live in the header, acting as concise summaries for search engines. Optimized meta tags provide Googlebot with clear and informative signals about your ecommerce pages, helping it understand your content quickly and accurately.
Now, there are a few meta tags every ecommerce business must focus on.
- Title tag (max 60 characters)
This is the headline of your page in search results. You should include relevant keywords and accurately reflect the content, but keep it concise and user-friendly.
- Meta description (max 160 characters)
This is a short blurb displayed under your title tag in search results. Highlight benefits and summarize content to entice users to click. You should keep it unique to differentiate yourself from competitors.
- Meta keyword tag
While not a direct ranking factor, meta keyword tags can enhance your visibility. Use relevant keywords naturally, avoid keyword stuffing, and focus on user intent.
5. Use XML Sitemaps
XML sitemaps act as a roadmap for Google, listing all the important pages on your ecommerce site along with key metadata. Sitemaps clarify the relationship between each URL on your site, preventing duplicates and ensuring they are correctly indexed and categorized. They also highlight blog posts, videos, and images you want indexed that Google may miss.
By providing a clear, up-to-date structure in the proper XML format, you significantly simplify Google’s works, and your site enjoys faster, more comprehensive indexing and, of course, better SEO results.
6. Make Each Product Description Unique
Well-written descriptions packed with relevant keywords help Google understand what you’re selling and categorize your products effectively—and this goes beyond just the title. Detailed information about features, materials, and uses paints a much clearer picture for search engines.
Remember, Google rewards originality. So, ditch the generic fluff and craft engaging descriptions that showcase your product’s value proposition. Think like a shopper and a search engine bot at the same time. Include details that would be helpful to both, and don’t forget descriptive alt text for your product images.
By investing in high-quality product descriptions, you’ll not only inform your customers but also help search engines understand your products, potentially leading to faster crawling, better categorization, and ultimately, improved SEO performance.
Optimized Ecommerce Site Structure Improves Google Indexing Performance
Ecommerce websites built with JavaScript can challenge Google’s crawling and indexing process. To address this, create a logically structured website using the six tips mentioned above.
To complement this approach, consider adopting Prerender—an enterprise SEO rendering solution. Prerender works by dynamically rendering your product pages ahead of time and feeding them to search engine crawlers upon request. This reduces Server Response Time (SRT) and ensures that all your SEO elements and the page’s content are 100% indexed. Ultimately, this allows you to leverage your SEO efforts on the product pages to improve their visibility and potentially boost their ranking in search results.
Sign up to Prerender today and get 1,000 free monthly renders!
FAQs
How Can I Get Google To Crawl My Ecommerce Site Better?
There are a few ways you can ensure that your ecommerce site gets crawled—and eventually indexed—more efficiently. These include:
- Use a clear site structure
- Create optimized XML sitemaps
- Use proper internal linking
- Ensure efficient JavaScript rendering with Prerender.io
- Manage faceted navigation well
Why Is Google Not Indexing All My Product Pages?
Common reasons for product page indexing issues include JavaScript rendering problems, poor site architecture, crawl budget limitations, and duplicate content. Learn more about how you can get your webpages indexed faster.
How Often Should Google Crawl My Ecommerce Site?
Crawl frequency depends on:
- Site size and updates
- Content freshness
- Site performance
- Technical optimization
Large e-commerce sites should aim for daily crawling of important pages.