Have you ever encountered a 404 error while browsing the web?
These “page not found,” or 404 errors are common, especially in single-page applications (SPAs). While there are a couple of traditional solutions to fix error 404, they often fall short due to the intricate nature of SPAs. Left untreated, 404 errors can frustrate users when accessing your page and damage your brand’s reputation.
This SPAs article will provide a comprehensive understanding of 404 errors on SPAs. We’ll start with understanding what a 404 error is and what causes it, then introduce you to a powerful solution that fixes error 404 effectively.
What is a 404 Error?
Before we dive into the specifics of 404 errors on SPAs, let’s understand the concept of 404 errors.
Essentially, a 404 error is an HTTP status code that indicates the server could not find the requested webpage. That’s why some called the 404 error ‘404 page not found.’
A 404 page not found error occurs for various reasons, such as mistyped URLs, broken links, or deleted content. Developers often create custom 404 pages by adding links to other pages, writing apology messages, or even turning them into humorous messages to reduce the impact on user experience.
Understanding 404 Errors on SPAs
SPAs built with JavaScript and its frameworks have gained popularity over the years. They deliver fluid, app-like experiences within browsers, enabling websites to load content dynamically. However, it also comes with drawbacks, namely challenges in handling URLs and responding to requests.
In a single page load, a SPA retrieves all necessary HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code, updating the content without requiring a full page refresh. This approach enhances user interaction and engagement but introduces complexities in managing URLs, especially when users navigate between different application sections.
What’s important to understand about 404 pages in SPAs is that SPAs only have one indexed page. So when users go with a route different from the indexed page, they will get a 404 error page.
Furthermore, unlike traditional multi-page applications, SPAs render JavaScript on the client side. This means that JavaScript manages navigation, interprets the URL changes, and fetches the necessary content without making a server request. While this enhances speed and responsiveness, it also means that the server may not be aware of all possible routes, eventually leading to 404 errors.
Some Common Causes of 404 Errors on SPAs
A. JavaScript-based navigation challenges
SPAs heavily depend on JavaScript for navigation. If JavaScript fails to load or execute routes properly, users may encounter 404 errors. This is because the client-side routing is unable to interpret and handle the URL changes.
B. SEO HTML status codes and their implications
Search engine crawlers may struggle to index SPAs due to the dynamic nature of the content loading. This can lead to search engines encountering 404 errors when attempting to crawl pages that haven’t been rendered or properly configured.
C. Crawling and indexing issues
Search engine crawlers, which traditionally rely on static HTML content, may not effectively navigate SPAs before ranking their pages. This results in 404 errors for users accessing those pages via search results.
Related: Learn how to optimize SPAs for crawling and indexing here.
Is a 404 Error the Same as a Soft 404 Error?
While a 404 page not found error is pretty straightforward, developers often encounter a more complicated variant known as a soft 404. A soft 404 error occurs when a server returns a 200 OK status code instead of a 404 error code, even though it’s an empty page or a page that doesn’t exist.
Although soft 404 SEO errors are not among the “official” SEO HTML status codes, they are common and can harm the SEO performance of single-page applications. When search engine bots try to crawl a page with soft 404 and get a 200 OK status code, it indicates that the page exists and will continue to crawl the page—wasting your limited crawl budget.
And since the page or some of its content is missing, the search engine may index an empty page with nothing to display on search results. This will waste your hard work and valuable SEO elements and ruin your user experience.
6 Methods to Resolve 404 Errors on SPAs
Here are some common solutions to fix error 404 on SPAs:
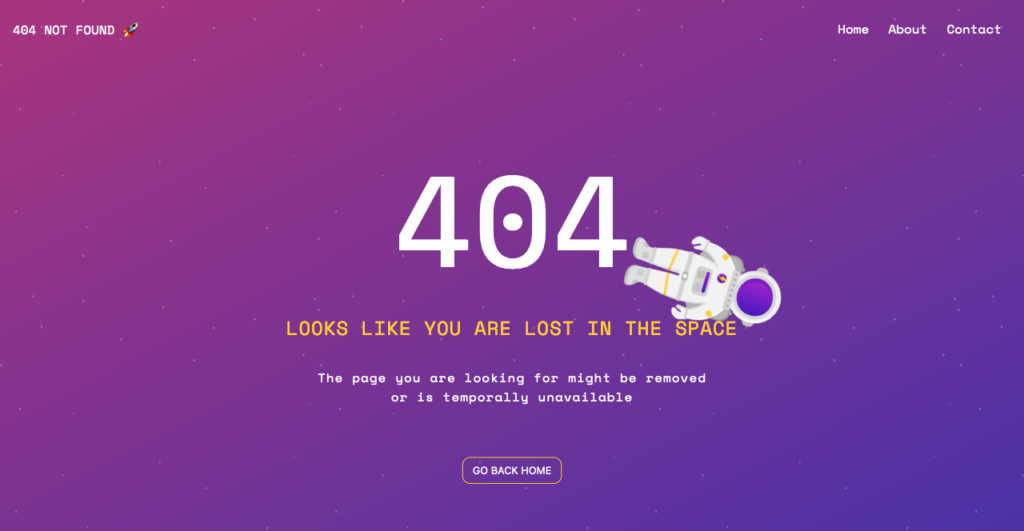
1. Redirect to a Custom 404 Page
Redirecting broken URLs to a dedicated 404 error page provides users with a consistent and user-friendly experience. This centralized approach to handling “page not found” errors also allows you to guide users back to relevant content or your homepage.
Here’s an example of Github’s custom 404 error page:
2. Proper Configuration of Routes
As we saw earlier, one common cause of 404 errors in SPAs is misconfigured routes. Developers must ensure that the application’s routing system accurately reflects the application’s structure. This includes defining routes for each section or page and handling variations such as nested routes.
SPAs often utilize dynamic route parameters to load specific content based on user input or selections. You must ensure the corresponding content is available to prevent 404 errors when users access pages with dynamic URLs.
Additionally, to fix error 404, you can redirect the page to another by implementing a 301 redirect. This informs search engines that the page has been relocated, preventing the display of a 404 error for an existing page.
3. Implementing Error Boundary Components
Incorporating error boundary components in the SPA can help catch JavaScript errors, preventing the application from crashing and displaying a generic 404 error. Certain client-side navigation libraries, such as React Router or Vue Router, offer mechanisms to handle 404-page not-found errors gracefully.
In React, you can define a route for 404 errors as follows:
<Route path=”*” component={NotFound} />
Get the full code examples of creating a catch-all route using React Router and redirecting undefined routes to a 404 page here.
4. Nginx Configuration for 404 Error
If you use Nginx to run your SPA, you can configure it to smoothly handle the 404 error redirection. Get the full code snippet on configuring Nginx here so that the request will always fall back to the index.html file if the requested URL can’t be found.5. Server-Side Rendering (SSR)
5. Server-Side Rendering (SSR)
Server-side rendering involves rendering pages directly on the server before sending them to the client, as opposed to relying solely on client-side rendering (CSR). SSR can enhance SEO by providing search engines with prerendered content, which also helps fix error 404 issues.
For single-page applications facing persistent 404 errors, integrating SSR can be a smart solution. By prerendering pages on the server, SSR ensures that search engine crawlers and users receive HTML content, reducing the likelihood of countering 404 errors due to client-side rendering issues.
However, SSR can be challenging to implement, especially for developers accustomed to client-side rendering. It also requires additional server resources, which can be very costly. Furthermore, SSR may not be a viable solution for SPAs that rely heavily on client-side rendering for dynamic content.
6. Dynamic Rendering Solution for SPAs
The best solution to fix 404 errors while also boosting SEO is using a dynamic rendering tool.
Prerender, for example, works by intercepting requests from search engine crawlers and serving them static HTML snapshots from a cache. This ensures that search engines receive the same content as users, eliminating the risk of 404 errors due to client-side rendering issues.
Not only that, Prerender also helps improve SEO performance. Since it provides search engines with crawlable content, it accelerates the indexing time and indirectly improves PageSpeed. Consequently, this will boost your SEO health and rankings, giving more visibility to your website.
Furthermore, as your website changes, your content will differ from what’s in the cache. Prerender addresses this through a feature called recaching. This allows developers to schedule Prerender to fetch pages, create new snapshots from updated content, and store them in the cache. This way, search engines will always receive the most up-to-date version of the pages, preventing issues with outdated information or missed optimizations.
As an enterprise SEO tool, Prerender is scalable, cost-effective, and requires no changes to your existing infrastructure. It gives SPAs a lot of benefits, which you can get by getting started with Prerender now.
Prevent 404 Errors for Better SEO Health
Resolving 404 errors is crucial for a smooth user experience and strong SEO performance. With the unique challenges SPAs face in handling URLs, you need to find the right solution.
While various methods exist, dynamic rendering with Prerender is one of the best solutions. It effectively fixes error 404 and also enhances SEO health by ensuring an accurate indexing process. With Prerender, you’re not just resolving issues—you’re optimizing your website for peak performance!
Make your SPAs deliver a flawless experience for users and search engines alike by adopting Prerender today. Start with a FREE 1000 renders per month!
Explore more about 404 Management:
- What Are Soft 404 Errors and How To Fix Them (5 Easy Ways)
- How to Optimize Single-Page Applications (SPAs) for Crawling and Indexing
- Robot.txt SEO: Best Practices, Common Problems & Solutions
FAQs on How to Solve 404 Error Pages on SPAs
Answering some common questions about 404 errors and how to fix them.
1. Are 404 Errors on SPAs Bad for SEO?
404 errors are not bad for SEO. In fact, it is common for large websites to have several 404 error pages as the content is always changing. Here’s exactly what Google says, “If some URLs on your site 404, this fact alone does not hurt you or count against you in Google’s search results” (source).
2. How Do I Know if a 404 Error Is a Client-Side or Server-Side Issue?
First, inspect the HTTP status codes. A 4xx signals it is a client-side issue, while a 5xx status tells you that it is a server-side problem.
3. What Tools Can I Use to Monitor 404 Errors on My Website?
You can use SEO auditing tools like Screaming Frog to check whether you have 404 errors on your site and they are properly redirected. If you don’t like the tool, here are 10 alternatives to Screaming Frog.
4. What Should I Include in a 404 Error Page?
There’s no rule on what to add to your custom 404 error page. However, most websites include the following content and SEO elements on their 404 page:
- A ‘404 page not found’ text.
- A short blurb to explain the ‘404 error’ situation. Make it fun with funny pictures or puns.
- Links to your pages, such as the homepage, top-performing blogs, or key landing pages.
5. 404 Error Page vs. 301 Redirects: What’s the Difference?
A 404 error page is a sign that a website cannot return a page because the page doesn’t exist anymore. It can be caused by a deleted page, mistyping the URL, or a broken link. This means that having 404 error pages generally won’t hurt your SEO performance.
301 redirects, on the other hand, is a permanent redirect from one page to another. This means that search engine crawlers will visit the original page and follow the 301 redirection path to the new URL. 301 redirects are used when you move or merge a page, allowing the link juice to continue boosting your SEO performance.Learn more about 301 redirects and how to properly apply the redirection here.