If you’ve ever browsed the internet, you have probably encountered a 404 error at some point.
A 404 error message can be helpful feedback for a web user, but using it in the wrong context can lead to a soft 404 error. A soft 404 error can negatively impact SEO performance, especially when a lot of them go undetected and they start to pile up.
To avoid this situation, developers should work closely with SEO experts to keep soft 404 error pages to a minimum.
Developers will want to work quickly. A soft 404 error can increasingly affect your website’s performance the longer it stays unresolved. In this guide, we will cover everything you need to know about soft 404 errors, from what the error is to how you can fix it, so that your site’s performance and rankings aren’t harmed.
What Is A Soft 404 Error?
A soft 404 error and a regular 404 error are often used interchangeably, but they mean different things.
The regular 404 error, sometimes called a 404 error or a hard 404, occurs when a webpage is unavailable. In that case, a server sends the correct HTTP status code, which returns a message to display on the browser: “404 Not Found.” This code implies that the page cannot be found.
So, then exactly what is a soft 404 then? A soft 404 error, on the other hand, occurs when the server sends a “200 OK” status for the web page, but Google mistakenly interprets the message to read that a 404 error should be displayed. Although it is a mistake on the search engine’s part, it usually happens when the page looks like an error.
This is where the confusion arises. The search engine marks a page as a “404 Not Found” page, even though that’s not the webpage’s correct status. If you are experiencing soft 404 errors on your website and these errors are displayed in tools like Google Search Console, you should take an immediate step to fix them.
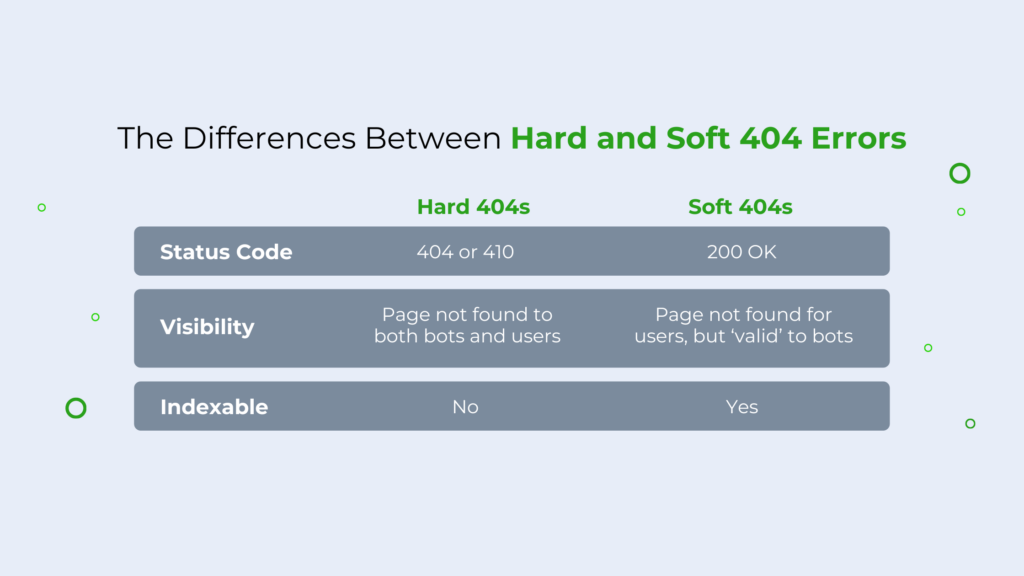
What’s The Difference Between Hard and Soft 404s?
There are a few key differences between a hard “404 Not Found” error and a soft 404.
The main one is the status code. The former has a status code of 404 or 410, which implies that the page cannot be found. In this case, a server sends the correct HTTP status code, which returns a message to display on the browser: “404 Not Found.” This code implies that the page cannot be found. The image below is of a hard 404.
With a soft 404 error, the page is still not found. But instead of returning the 404 or 410 code, a “200 OK” code is returned. When users encounter a soft 404, they receive a 200 response code and are likely redirected to the homepage.
Additionally, hard 404s aren’t indexed by search engines. Soft 404s are indexable and can show up in SERPs. While Google is unlikely to feature soft 404s in search results, this isn’t to say that other search engines won’t.
While hard 404s aren’t bad, soft 404s can be a confusing situation for both users and search engines. This is why it’s best to keep them to a minimum.
What Causes Soft 404s?
Soft 404s can be caused by various reasons, such as:
Thin, Duplicate, or Weak Content
Weak content is one of the primary causes of a soft 404. If the page has little to no content, or if it’s a duplicate, search engines may default it to a status code of “404 Not Found.” Even when the status response is valid, search engines may still display the 404 error.
Some examples of a soft 404 error due to lack of content include:
- Empty product category pages
- Empty blog category pages
- Empty search result pages
If poor quality content is the cause of your soft 404s, not to worry—this is typically a relatively easy fix. You’ll find tips for this further below in this article.
The Redirect Target Is Not Relevant Enough
If you are redirecting from one URL to another, it must be relevant. Otherwise, search engines will display a “404 Not Found” message.
This is common with ecommerce sites that redirect to another product or category that’s irrelevant to a search engine’s algorithms.
You’re Blocking Search Engines From Rendering
Sometimes, a soft 404 error can happen when you’ve blocked search engines from accessing your JavaScript or CSS files. These files are used to render pages. If search engines can’t access them, then it may lead to a soft 404 error.
This issue can be resolved by debugging and verifying your webpage via Google’s inspection tool.
Pages Contain 404-like Phrases
If your page has phrases that are primarily found on a 404 page, it can cause a soft 404 error.
When possible, mitigate the use of phrases you would find on a 404 error page, such as:
- “Not in stock”
- “Does not exist” or
- “No longer available”
These phrases can be mistaken for a 404 page. Avoiding these on your site unless necessary is a simple way to help prevent soft 404s.
Other Technical SEO Issues
Additional causes of soft 404s include: outdated links, redirects that haven’t been established yet, temporary crawling issues, or poorly configured servers.
Google can also falsely marking pages as soft 404s for no apparent reason—especially for JavaScript sites. This is why it’s crucial to monitor your JavaScript site’s technical SEO on a frequent and regular basis.
Related: 8 JavaScript SEO Problems and How To Solve Them
What Is An Example Of A Soft 404 Error?
When a user searches for something on your website that does not exist, they will get a “Not Found” message, which a search engine may misinterpret. This is what happens in a soft 404 error.
With a soft 404, the server response code is “200 OK,” but the search engine still thinks that there is a query on your page. Therefore it erroneously interprets the page as a 404 error.
If you are trying to access a page that exists in the CMS, but is still not being displayed by Google, chances are it is due to a soft 404 error.
If the category page does not have any content under the category, it will likely lead to soft 404 errors. Even when the webpage exists on the website, if there is no content, Google will interpret the page as a blank and displays a 404 error.
How Google Sees Soft 404s
Google has changed the way it handles soft 404 detection and classifications.
Google now looks at each page by device type and assigns a soft 404 classification differently to the same URL on desktop and mobile. If Google sees a URL and accesses the same URL on desktop and mobile, it may return a soft 404 error on mobile and desktop, or vice versa.
This means Google now detects a soft 404 status on a URL, as it goes through a URL. It also does so by device type.
This can be a problem when the page works correctly on a mobile Search Console, and does not throw any alerts. Meanwhile, some of your pages may be experiencing soft 404 errors outside of the console. This can affect your website’s performance and rankings.
Disadvantages of Soft 404s and Why They’re Bad for SEO
While there’s no official penalty for soft 404s, soft 404 errors can negatively impact your SEO—especially when they start to pile up.

Here are a few reasons why they’re problematic.
Wasted Crawl Budget
Soft 404s can quickly waste search engines’ crawl budgets on pages with little or no value. This is one of the main disadvantages of soft 404s.
Search engines have a limited crawl budget—you don’t want to waste this on pages that aren’t important. Using up this crawl budget on unnecessary pages then leads to the slower discovery of new content. And as a result, this can delay the indexing of much more important pages on your site.
Related: free downloadable on why crawl budgets matter for SEO success.
Reduced Site Quality
Having many 404 errors can signal to search engines that your site isn’t well-maintained—even if that’s not the case. This can have a negative impact on your site’s rankings in SERPs.
Having a soft 404 doesn’t mean that your site is low quality. However, Google prioritizes sites that are high-quality, feature genuinely helpful content, and promote a good user experience.
If you leave your soft 404s unresolved, this can send the opposite message across. As a result, Google may be unlikely to favor your site highly in SERPs.
Indexing Issues
Since soft 404 pages return a 200 HTTP status code, they’re considered indexable by search engines. As such, they may be indexing pages that shouldn’t be indexed.
For example, you probably don’t want an empty product page with a soft 404 to be indexed. This doesn’t put your brand in the best light. Instead, you’ll want that product page to be updated, de-indexed, or deleted entirely.
While Google states that it is unlikely to feature soft 404s in SERPs, soft 404s are technically indexable and can appear in search results. Because of this, it’s not worth the risk to your brand, and you should resolve them as soon as possible. That way, you can index pages that are truly valuable to your company.
Related: 10 Ways to Accelerate Website Indexing
Poor User Experience
This is one of the main disadvantages of soft 404s. When a user lands on a soft 404 page, they’ll likely receive a 200 Message and will be redirected back to the homepage, as there isn’t an error page to land on like with hard 404s.
This can be a frustrating, confusing experience for users, and can reinforce a negative brand perception if your site has too many. As a result, soft 404s could contribute to higher bounce rates, lower conversion rates, and poor user experience overall—all of which can negatively impact your rankings and sales.
Diluted Link Equity
When links pass to soft 404s, your link equity is wasted on more valuable content. Instead of strengthening relevant pages, link equity is distributed to non-existent or irrelevant content. This can frustrate users, hurt your site’s performance, and impact your site’s authority in the eyes of search engines.
Search engines use links as valuable roadmaps to understand your site, so it’s ideal to ensure that any backlinks are accurate, up-to-date, and optimized.
Related: How to Optimize Your Crawl Budget with Internal Links
How To Find Soft 404 Errors
Finding soft 404s isn’t particularly challenging. An easy way is to log into Google’s Search Console, visit the Pages screen, and scroll to the bottom. You’ll see any soft 404s listed there.
You can also use Screaming Frog to find broken links on your site, as it identifies websites that have linked to pages that no longer exist. Another alternative to Screaming Frog is Xenu Link Sleuth.
For hard 404s, you can use Prerender’s 404 Checker tool. Log into your Prerender account and access it on the left-hand side of the dashboard. Don’t have a Prerender account? Get started with 1000 URLs for free.
How To Fix And Resolve Soft 404s

Not all 404s are bad, as there are cases when they are displayed in the correct context. When a product is not available, for example, displaying a 404 error page lets users know that the particular product is permanently removed from the website.
Soft 404 errors can be tricky, however. There can be cases when a webpage is not valid and a server still returns a “200 OK” status. In these cases, you should look at the errors and try to fix them.
Here are some solutions for addressing soft 404 errors.
1. Confirm It’s Actually a Soft 404
Make sure you’re actually dealing with a soft 404—not a false alarm. In most cases, a page incorrectly marked as a soft 404 error by Google Search Console can be audited and verified.
Here’s how:
- Go into Google Search Console and click on the “Submitted URL seems to be a soft 404” button from the Coverage Report. This returns a complete list of soft 404 pages.
- Open the URLs in new tabs.
- If the page is a valid part of your website and you want it to appear in the search results, choose the “Validate Fix” option. This will make Google crawl the page and update the status code.
- Once complete, inspect the page and test the live URL.
Alternatively, you can select the URL and click on the “Inspect URL” option.
This will give you more information about the page of interest and give you an option to “Request Indexing.”
Before doing so, test the live URL to allow Google to refresh its report. Doing this will give you the correct status of the page. In most cases, the page will function correctly and require no changes.
2. Update and Refresh Page Content
If your page exists but search engines are reporting it as a soft 404, it may be due to thin content.
In this case, update and improve the page content and resubmit it for indexing. Once updated, the page will become more crawable, helping to eliminate the soft 404 error.
For example, if you’re updating product pages, consider adding:
- High-quality images and videos
- Substantial, informative copy
- Clear CTAs
- FAQs and more
Related: more tips on how optimize your product pages for search.
Another point to note: crawlers may be reporting the page as a duplicate. If that’s the case, fixing these can be a quick and easy win for your SEO performance. Learn how to fix duplicate pages here.
3. De-Index Them from Search Engines
Another solution is to keep the page on your site but de-index it from search.
Adding a no-index directive in the header will instruct the search engine not to index that particular webpage on the site. This will allow you to fix the soft 404 error, since Google won’t display the page under the Error report.
Note: you will still see this page listed in the excluded report under the soft 404 section.
4. Configure Them to Proper Error Codes (404/410)
If the page isn’t available or invalid, try configuring your site to return the correct status code.
Configuring your site to return a 404 code for invalid pages might mean deleting the affected pages. Once you delete a page, the HTTP server will show a hard 404 code when the page is requested, allowing you to minimize your soft 404s.
Once you’ve configured your website for the correct code, resubmit the page to Google for indexing. It should help you get rid of the soft 404 error.
5. Use 301 Redirects
The last method to resolve the soft 404 error is by redirecting the page of interest to a valid page. You can do this by adding a 301 redirect into your .htaccess file.
This tells the search engine that the page is moved to a new location and ensures it does not display the 404 error for an existing page. Be sure to check that both of the pages have similar content before you redirect one to another.
While redirects themselves aren’t generally harmful for SEO, be cautious of how many redirects you use in a link chain. Too many in one chain can negatively impact your SEO.
Related: What Are Redirect Chains And How To Fix Them
How to Prevent Soft 404s: Technical Site Maintenance
Regular site maintenance is the easiest way to keep errors at bay, ensure that soft 404 errors don’t negatively impact your site, and make your site accessible for visitors.
Along with foundational tools like Google Search Console and Screaming Frog, you should use a variety of technical SEO platforms. One to consider is Prerender.io, especially for large JavaScript sites that struggle with crawling and indexing issues.
Prerender is a pre-built rendering solution that converts your site’s JavaScript content into HTML, a format that search engines can easily read. This solution is much more cost-effective and efficient than server-side rendering (SSR). And as a result, you can efficiently improve your crawling and indexing performance in a matter of weeks.
Prerender is trusted by 65,000+ global brands, including Salesforce, Walmart, and Wix. Get started with 1000 free renders today.
Frequently Asked Questions
TL;DR: What’s The Difference Between Soft and Hard 404s?
The main difference is the status code. Hard 404s have a 404 or 410 status code, implying that page cannot be found. Soft 404s have a 200 OK status code, meaning that they’re valid for search engines, but not for users.
What Happens When A User Lands On A Soft 404 Page?
They’ll likely receive a 200 message and be automatically redirected back to the homepage. They don’t land on a hard 404 page, so this can be a confusing experience for the user.
Do Soft 404s Show Up In Search Results?
Yes, soft 404s are indexable and still can appear in SERPs. As such, you can still face indexing issues if you leave soft 404s unresolved for long, which is why you should address them quickly.
Will Fixing Soft 404s Improve My Site Traffic?
Indirectly, yes. Resolving soft 404s can help boost your traffic. Fixing soft 404s ensures that crawl budgets aren’t wasted on invaluable pages, and helps make sure that important content shows up higher in SERPs.
Why Should You Fix Soft 404s?
You should resolve soft 404s quickly because they can waste crawl budgets, contribute to indexing issues, signal to search engines that you have a poor quality site, lead to a poor user experience, drive higher bounce rates and lower conversion rates, reduce link equity, and more.
How Quickly Does Google Detect And Report Soft 404 Errors?
Google typically detects soft 404 errors during its regular crawling process. The time it takes can vary, but you may see these errors reported in Google Search Console within a few days to a couple of weeks after they occur.
Can Soft 404 Errors Affect My Site’s Mobile Rankings Differently Than Desktop?
Yes, Google now detects soft 404 errors separately for mobile and desktop versions of a page. This means a page could be flagged as a soft 404 on mobile but not on desktop, or vice versa, potentially affecting your mobile and desktop rankings differently.
How Many Soft 404 Errors Are Too Many?
There’s no specific number, but even a few soft 404 errors can impact your site’s performance. It’s best to address them as soon as they’re detected. If more than 5-10% of your pages are showing soft 404 errors, it’s definitely time for immediate action.
![An image for the blog titled "What Are Soft 404 Errors And How to Fix Them [5 Easy Steps]". The image is light green with a yellow graphic that says "404."](https://prerender.io/wp-content/uploads/soft-404-errors-and-seo.jpg)