Why do my site pages keep getting deindexed?
Getting your content deindexed by Google is devastating for any SEO manager or content marketer. When a page is deindexed by Google or other search engines, it no longer appears in SERPs, costing you valuable visibility, clicks, and conversions. But what exactly causes deindexation?
Google may remove pages or URLs that violate its guidelines, even due to seemingly minor changes. Adjustments to site settings, content, or on‑page and technical SEO elements can cause your site to stop providing satisfactory answers to search queries. Google might also interpret these changes as attempts to manipulate its algorithm or engage in deceptive practices.
We’ll explore over 12 common reasons why Google may deindex your content. We’ll help you identify and fix these issues to maintain strong technical SEO. Plus, we’ll recommend useful tools, such as SEO monitoring and prerendering tools, to reduce the risk of deindexation.
Reasons Why Your Content is Being Deindexed
There are various causes why Google and other search engines deindexed your site’s pages and content. This includes technical SEO and crawlability issues, structured data problems, and Google detects deceptive SEO practices.
1. Using Cloaking Techniques
The first reason on why your page getting deindexed is cloaking. Cloaking involves showing different content or URLs to users and search engines to manipulate how your pages rank on SERPs. This practice violates Google’s Webmaster Guidelines and totally goes against Google’s goal of providing relevant results to searchers.
If you try manipulating the system with cloaking, Google will quickly catch on and penalize your site. In most cases, your URL gets deindexed. Honesty and transparency are essential for a healthy online presence.
Related: Is dynamic rendering cloaking? This cloaking vs dynamic rendering blog gives you the answer.
How to Get Indexed Without Risking Cloaking Penalties
Start by checking if cloaking is actually the problem. Here’s how to do it.
Head over to Google Search Console, click on Manual Actions and see if there’s a warning about “Cloaking” or “Sneaky redirects.” If there is, Google has flagged your site for showing different content to users and bots.
To dig deeper, use the URL Inspection Tool to see what Googlebot sees. Then open the same page in your browser and view the source. If the two versions don’t match, especially if one has missing links, swapped content, or strange redirects, you’ve probably got cloaking in place. Fix it by removing whatever is causing the difference, whether it’s a user-agent check, JavaScript swap, or crawler-only redirect.
Make sure everyone—Google included—gets the same version of your page. Once that’s done, double-check your fixes with the Inspection Tool.
If things look good, submit a reconsideration request and explain what you changed. It’s important to be honest and clear, as Google wants to know you’ve actually solved the issue.
To avoid future problems, it’s smart to document how content is rendered and even run visual checks comparing Googlebot and real users during deployments. If you need different HTML for performance reasons, that’s okay, but use dynamic rendering the right way, and never hide or change core content.
2. Blocking JavaScript-Based Content
One technical issue that can inadvertently contribute to deindexing is blocking search engines from accessing and rendering your website’s JavaScript SEO content. This issue primarily occurs when using modern JS frameworks like React, Vue, or Angular, which default to client-side rendering.
As a result, your content becomes invisible to search engines, reducing your site’s appeal and negatively impacting its SEO. This can lead to Google deindexation on the affected pages or the entire site.
To resolve this issue, consider installing a prerendering SEO tool like Prerender. Prerender generates a static version of your pages and delivers it to search engine crawlers upon request. By doing so, you ensure that Google regains access to your content, allowing your pages to be indexed fast and perfectly.
Learn more about how to install Prerender and all the benefits you can enjoy with this prerendering SEO tool.
How to Get Google to Index Your JavaScript Content
We recommend adopting Prerender.io. Prerender.io makes your content easier and faster for Google to understand. It ensures your pages show up properly, even if they’re built with complex technology. The result? Your site is more likely to appear in search results—and not just google search results, but also in AI-based search platforms like GPT, Claude, Gemini, and Google’s AI Overviews.
Think of it as giving Google a clean, easy-to-read version of your website. If your content was hidden before, Prerender.io helps bring it back into the spotlight. You don’t have to change how your site works—just add Prerender for free today, and it handles the rest. More visibility, better rankings, and a real shot at getting featured in AI-generated answers.
Watch this video to learn more about Prerender.io JavaScript rendering solution and its SEO benefits:
3. Implementing Faulty Structured Data
Google’s structured data guidelines strictly prohibit any misleading or deceptive use of markup. For instance, if you own an ecommerce online store, you add fake star ratings to your product page’s rich snippets on SERPs.
Violating these guidelines by marking up hidden content, providing false information, or manipulating markup to gain rich results you don’t qualify for is considered a spam tactic. Even unintentional violations can lead to Google penalties, including deindexing from search results.
How to Fix Incorrect Structured Data
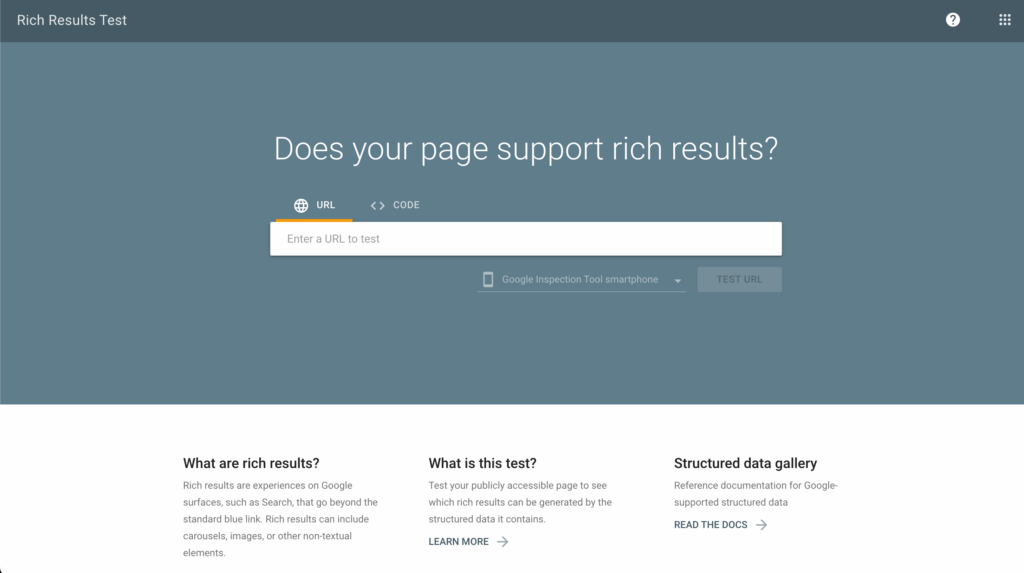
If you think your site might be using structured data the wrong way, like adding fake star ratings or marking up content that visitors can’t see, the first step is to double-check. Use Google’s Rich Results Test to scan a page and see if anything’s flagged. If you find markup that doesn’t match what’s actually on the page, remove or fix it.
For example, if your product doesn’t have real reviews, don’t try to add star ratings just to stand out on Google. It might seem like a small thing, but misleading data can hurt your rankings or even get your page removed from search results entirely.
Once you’ve made the necessary changes, run the test again to confirm everything looks good. You can also use the URL Inspection Tool in Search Console to see how Google sees your updated page. If you were hit with a manual action, you’ll need to request a review and explain what went wrong and what you’ve done to fix it.
4. Having Excessive Automated Queries to Google
Google has boundaries that you must respect. Sending automated queries or requests without permission is a no-go, as it violates their terms of service.
Google vigilantly monitors excessive, unauthorized traffic that strains its resources and may issue an IP block or deindex-related website URLs (or even the entire site) as a penalty.
Avoid accidentally triggering this by misusing tools or misconfiguring crawlers or web scrapers. For instance, aggressively scraping Google’s search results or proprietary data feeds using automated scripts is a violation.
How to Avoid Excessive Google Queries
The first step is to identify the source of the activity. Check your server logs or analytics tools for patterns of automated requests, especially those targeting Google services like search results or API endpoints.
If you’re using SEO tools, monitoring scripts, or web crawlers, make sure they’re configured correctly and not making frequent, unauthorized calls to Google. Disable or reconfigure anything that might be sending automated requests at scale, especially if you’re scraping Google search pages directly, which goes against their terms.
Once the offending scripts or tools have been corrected or removed, give your site a bit of breathing room. If your IP has been blocked or your pages deindexed, you’ll need to wait for the block to lift (which can take a few days or longer), or in some cases, submit a reconsideration request in Google Search Console if you received a manual action.
Once that’s done, make sure any automation you use going forward respects Google’s terms of service. If you need to pull data, use official APIs where available, set proper rate limits, and avoid scraping Google search directly. Keeping your activity clean and respectful is the best way to stay visible in search.
5. Participating in Link Schemes
While link building is an essential SEO strategy, you must exercise caution and avoid deceitful tactics. Google’s algorithms can spot unnatural link patterns and penalize sites or deindex URLs or domains that engage in manipulative link-building practices. For instance, participating in link schemes or buying links can lead to severe penalties.
Google also has a clear and strong stance against:
- Paid links are intended to manipulate search results.
- Low-quality link directories.
- Hidden links in footers.
- Keyword-stuffed links in comments and forum signatures.
Related: Learn about how to find and fix broken backlinks.
How to Recover from Link Scheme Penalties
If you think your site might be getting penalized for bad link-building practices, start by reviewing your backlink profile.
You can use tools like Google Search Console, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to see which sites are linking to yours. Look out for red flags, such as lots of links from spammy websites, keyword-stuffed anchor text, or links that seem completely unrelated to your content. If you spot anything suspicious, reach out to those site owners and ask for the links to be removed. For links you can’t remove, use Google’s Disavow Tool to tell Google you don’t want them to count those links against you.
After cleaning up your backlink profile, be sure to focus on earning links the right way. That means creating helpful, original content people naturally want to reference, not trying to game the system. Avoid paying for links or adding links in places just to manipulate rankings, like comment sections or footers. Honest, high-quality link-building always wins in the long run.
6. Having Faulty Redirects and HTTP Status Errors
Correct HTTP status codes are essential when implementing redirects. Using temporary redirects (302) instead of permanent redirects (301) can confuse search engines and cause indexing problems. If Google detects a redirect leading to a non-existent or error page, it may remove the original URL from its indexation list.
Moreover, URLs that consistently return error status codes like 404 (Not Found) or 500 (Server Error) are deemed “dead ends” by Google and eventually dropped from the index.
Also, keep in mind that domain expiration can make your URL unavailable for Google to crawl, and if there’s nothing to crawl, there’ll be nothing to index. So, ensure proper redirect management and timely domain renewal to avoid these problems.
How to Prevent Indexing Issues from Redirects and Errors
Start by checking your site for broken pages, bad redirects, and server errors. Focus on finding pages that return 404 (Not Found), 500 (Server Error), or use incorrect redirects like 302s where 301s should be used.
If you’ve redirected an old page but used a temporary (302) redirect instead of a permanent (301), Google may not transfer SEO value correctly, or may not index the destination page at all. Update these to proper 301 redirects to maintain link equity and indexing stability. Follow our guide to set up the 301 redirect chains correctly.
Next, fix any pages returning error codes. For 404s, either restore the content, redirect the URL to a relevant page, or serve a helpful custom 404 page that guides users back. This 404 error guide will show you how. For 500 errors, check your server or hosting provider for stability issues or misconfigurations.
Also, make sure your domain hasn’t expired. It sounds simple, but your pages will drop from the index if Google can’t access your site due to an expired domain. Once all issues are fixed, request a recrawl in Google Search Console to speed up reindexing. Good redirect hygiene and error-free pages are key to keeping your site healthy in Google’s eyes.
7. Using Doorway Pages
Creating low-quality pages solely to rank high for specific keywords and then redirect users elsewhere hurts your site in two ways. First, it delivers a frustrating experience for visitors who land on irrelevant content. Second, these pages clutter search results (SERPs) with useless information, making it harder for genuine searchers to find valuable websites.
Consequently, Google identifies and penalizes these doorway pages by either deindexing them or applying site-wide penalties that impact the ranking of all pages on your domain, not just the offending doorway pages.
Focus on generating unique, high-quality content that enhances user experience, consolidates similar content, and complies with Google’s guidelines to preserve your site’s integrity in search rankings.
How to Avoid Doorway Page Penalties
First, you need to identify any pages created just to rank for specific keywords that don’t offer real value to users.
These might be pages that target slightly different keyword variations but lead to the same or similar content, or worse, redirect users to a different destination altogether. Remove or consolidate these pages into more helpful, comprehensive content that genuinely serves the intent behind those searches.
Google values pages that solve a problem or answer a question, not pages that exist just to attract clicks. Not sure what Google likes? Here’s how Google defines quality content.
Once you’ve cleaned up the low-quality pages, focus on improving your site’s overall content strategy. Group similar topics into stronger, more useful pages instead of spreading them across thin, repetitive ones. Make sure every page has a clear purpose and offers real value to your readers.
8. Misuse of the Robots.txt Files
The robots.txt file directs search engines on how to crawl your site. However, incorrectly configuring this file can block Google’s bots from crawling and indexing your site.
A common error is the blanket ‘disallow’ rules (Disallow: /), which can exclude important pages or URLs from being indexed by Google. Another example is accidentally blocking folders that contain important pages—like Disallow: /blog/—which can stop Google from discovering your valuable content.
It’s also important to clear up a big misconception: blocking a page in robots.txt doesn’t automatically remove it from Google’s index. It just stops the page from being crawled. If Google already knows about the URL from other sites or internal links, it may still appear in search results, but without a proper title or description.
If you’re unsure how to configure your site’s robot directive, refer to our guide on robots.txt file optimization. This guide tells you everything you need to know about configuring your robots.txt files to avoid indexing issues and ensure Google discovers pages that matter to your business.
How To Properly Set Up Robots.txt Files
You can start by checking your existing robots.txt file by visiting yourdomain.com/robots.txt. Look for overly broad rules like Disallow: /, which blocks all pages from being crawled, or specific folders like Disallow: /blog/ or Disallow: /products/ that might be preventing Google from accessing key content.
If you spot any rules that don’t reflect your current SEO goals, update or remove them immediately.
Next, test your changes using the robots.txt Tester tool in Google Search Console. This tool helps you verify which URLs are currently blocked and whether your new rules are working as expected. Once corrected, request a re-crawl in Search Console to help Google rediscover and reprocess the previously blocked pages.
Learn more about robots.txt best practices and pitfalls here.
9. Having Malware or Security Issues
One of your top priorities should be ensuring the safety and security of your website for visitors.
Suppose Google detects that malicious actors have compromised your site and are serving malware, phishing pages, or other shady code that puts users at risk; they will promptly deindex those affected pages to prevent further harm. This action aligns with Google’s commitment to delivering a safe browsing experience.
To avoid deindexing due to such compromises, regular security audits, prompt software updates, vulnerability patching, and robust security practices like web application firewalls and HTTPS are crucial.
Related: Visit our How to Conduct A Technical SEO Site Audit blog to learn more about website auditing.
How to Keep Your Site Safe from Malware and Security Breaches
If Google has flagged your site for malware or security issues, act fast. First, check for warnings in Google Search Console under the Security Issues tab. This shows you the exact problem—whether it’s malware, phishing content, or hacked pages.
Next, scan your website using security tools like Sucuri SiteCheck, Wordfence (for WordPress), or your hosting provider’s built-in scanner. Identify and remove any malicious code, suspicious files, or unknown plugins or scripts that could have been injected by attackers.
After cleaning your site, update all software—CMS, plugins, themes, and server software—to close any security gaps. Set up HTTPS, enable a Web Application Firewall (WAF), and strengthen passwords and user permissions.
Then, after fixing the issues, go back to Search Console and request a review. Be clear about what steps you took to resolve the problem. Google will recheck your site, and if everything looks safe, your pages can be reindexed. Regular security audits and updates are your best defense. Don’t wait until Google sounds the alarm.
10. Having Hidden Text or Links
Discovering hidden text on your website can raise Google’s attention, but not all instances are intentionally deceptive. Sometimes, the hidden text serves a legitimate purpose. For example, the alt text that describes images or the descriptive captions for videos.
However, there are instances where they are used sneakily to deceive readers or even Google. Some examples of such tactics include:
- Setting the font size to zero renders the text invisible to users.
- Positioning text off-screen using CSS makes it inaccessible to visitors.
- Displaying white text on a white background effectively conceals the content.
- Using small, inconspicuous characters to hide links, misleading both users and search engines.
While innocent instances of hidden text might require adjustments to regain Google’s trust, engaging in deceptive practices is a surefire way to get your website deindexed.
How to Resolve Hidden Text and Link Issues
Use tools like Google Search Console’s URL Inspection Tool or a browser’s “Inspect Element” feature to review page elements. Look for common red flags: text with a font-size: 0, white text on a white background, or off-screen positioning using negative margins or display: none.
If the content isn’t meant to be seen by users but is loaded with keywords or links, remove it immediately. Even if it wasn’t added to manipulate rankings, Google may still treat it as a violation.
Next, clarify which types of hidden content are safe, such as alt text, ARIA labels, or content inside tabs or accordions that users can access through interaction. Make sure all hidden content serves a real user purpose and isn’t there just for search engines. Transparency is key: if your users can’t see or interact with it, it probably shouldn’t be there.
11. Using Improper Canonicalization
When several pages or URLs of your site are very similar, they can lead to duplicate content issues. If you fail to specify the correct canonical URL using the rel=”canonical” tag, Google will receive conflicting signals about which page or URL is most important.
Because of this confusion, Google ultimately chooses and indexes one page or URL as the original version and ignores the others, which can hurt your site’s search visibility.
Suppose Google perceives the duplicate content as an attempt to manipulate search rankings; it may not only ignore the pages but also remove them from its index altogether. In other words, it gets deindexed.
How To Set Up Proper Canonicalization
To avoid this, always set a clear canonical tag on pages with similar or duplicate content. For example:
✅ Correct canonical usage
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.example.com/shoes” />
This tells Google that https://www.example.com/shoes is the preferred version.
❌ Incorrect canonical usage
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.example.com/” />
This sends all your product pages to the homepage, confusing Google and potentially deindexing important content. Using canonical tags correctly ensures Google knows which version of your content matters most, without hurting user experience or risking deindexing.
Canonical vs. Redirect vs. Noindex
|
Feature |
Purpose |
User Experience |
Ideal Use Case |
|
Canonical Tag |
Suggests the preferred version of a page |
Page still loads |
Similar content on multiple URLs that should rank as one |
|
Redirect (301) |
Sends both users and bots to another URL |
User is redirected |
When you permanently move a page or consolidate duplicate pages |
|
Noindex Tag |
Tells Google not to index the page |
Page still loads |
For pages you don’t want in search (e.g., thank-you pages) |
12. Experiencing Slow Server Response and Loading Times
A slow-loading website with a slow server response can hinder Google’s crawling and indexing process, consuming more time and resources. This signals to Google that your site may provide a poor user experience, which could frustrate and drive users away.
Pro tip: Find out how to improve your Google PageSpeed Insight scores to 100 points.
Because Google only has limited resources to crawl and index all available content (also known as the crawl budget) on the internet, it prioritize which content worth visiting. If your site consistently drains resources, Google is more likely to deprioritize and deindex your content over time.
How to Increase a Website’s Loading Times
Start by running your key pages through Google PageSpeed Insights or Lighthouse to identify performance issues. Look out for slow server response times, unoptimized images, render-blocking scripts, and excessive JavaScript.
These issues don’t just slow down your site. They eat into your crawl budget, making it harder for Google to discover and index your pages efficiently. Addressing even a few of these issues—like compressing images, reducing unused JavaScript, or enabling lazy loading—can have a noticeable impact on speed and crawlability.
For websites built with JavaScript frameworks like React, Vue, or Angular, you can use Prerender.io to generate a static version of your dynamic pages specifically for search engines. This makes your content easier and faster for Google to read, even if your site is JavaScript-heavy.
The result? Google crawls your site more efficiently and indexes your pages faster—some Prerender customers have seen up to 300x better crawling and 260% faster indexing. If page speed is holding your site back, Prerender is one of the simplest and most effective ways to fix it.
How to Prevent Getting Deindexed by Google: Best Practices
A. Follow Google’s Quality Guidelines
Always prioritize high-quality, original content that serves your audience’s needs and avoid tactics like keyword stuffing, cloaking, doorway pages, hidden text, or buying backlinks.
These shortcuts might offer temporary gains, but they violate Google’s Webmaster Guidelines, and penalties often result in loss of rankings or deindexing. Instead, focus on writing for humans first—answer their questions, solve their problems, and keep your content updated and relevant.
B. Stay Away from Spammy Schema Markup
Structured data helps enhance your search listings (like showing star ratings, FAQs, or product details), but misusing it can lead to penalties. For example, marking up fake reviews or using schema types that don’t match the page’s purpose violates Google’s structured data policies. Use Google’s Rich Results Test to validate your markup and only tag information that’s actually visible and accurate.
C. Avoid Excessive or Unnatural Internal Linking
Internal links are great for SEO when used naturally. But over-optimizing anchor text, stuffing internal links into footers, or using the same keyword-rich anchor repeatedly can trigger penalties. Make sure your internal linking is user-focused, help visitors navigate your content logically. A well-structured site helps Google understand your content hierarchy without raising red flags.
D. Monitor Manual Actions and Security Alerts in Google Search Console
Google often provides early warnings if something’s wrong, like unnatural links, spammy content, or a security breach.Visit Search Console > Manual Actions and Security Issues regularly. If you see any warnings, address them immediately and submit a reconsideration request. Think of Search Console as your direct line of communication with Google; it tells you what’s working and what’s hurting your site’s visibility.
Avoid Getting Deindexed By Google Through JavaScript Rendering
Unless it’s a deliberate attempt to remove a URL from Google search results, getting deindexed is a worst-case scenario for any website. And by worst case, we’re talking about a full-blown impact that can crush your site’s visibility and drown your online revenue.
To avoid this fate, proactively stay on top of your SEO game and follow Google’s guidelines to a T. Regularly audit your site, monitor indexation rates, and deliver awesome user experiences with high-quality, original content.
To make your SEO journey smoother, follow our 10-step checklist of excellent SEO indexing methods to help Google find and index your site. And combine this with Prerender adoption, as Prerender can help you to:
- Identify and solve crawl errors and page indexing issues from the root.
- Optimize your crawl budget and feed bots with index-ready files.
- Access additional technical SEO services, including sitemap crawling and 404 checkers.
With Prerender, you ensure that your content is crawled, indexed, and found by Google and customers alike.
Sign up today and get 1,000 free monthly renders to boost your page visibility.
FAQs – How To Prevent Getting Deindexed by Google
Why Is Google Deindexing My Pages?
Google might deindex pages for several reasons: low-quality or thin content, duplicate content, technical issues preventing proper crawling, accidental noindex tags, or pages that provide little to no value to users. Check your robots.txt, meta tags, and site quality to identify the cause.
Will Deindexing Pages Affect My Overall Site’s SEO?
Strategic deindexing of low-value or duplicate pages can actually improve your site’s SEO by helping search engines focus on your most important content and preserving crawl budget.
Should I Use Robots.txt Or Noindex Tags For Deindexing?
Noindex tags are generally more reliable for deindexing as robots.txt only prevents crawling, not indexing. However, both methods can be used together in specific situations.
How Can I Speed Up My Webpage Indexing?
Several strategies can accelerate indexing:
- Use a solution like Prerender.io to ensure search engines and AI crawlers can easily access and render your content
- Submit your sitemap through Google Search Console
- Improve page load times and optimize Core Web Vitals
- Ensure proper internal linking structure
- Use the URL Inspection tool to request indexing for important pages
- Fix any technical issues preventing efficient crawling